Three mainstream fertilizer granulators: Core equipment for different production needs
Fertilizer granulators are the core equipment for granular fertilizer production. Rotary drum granulators, double roller press granulators, and disc granulators are the three most widely used models, each with its own focus on granulation principles and performance, adaptable to different raw materials and production capacity requirements.
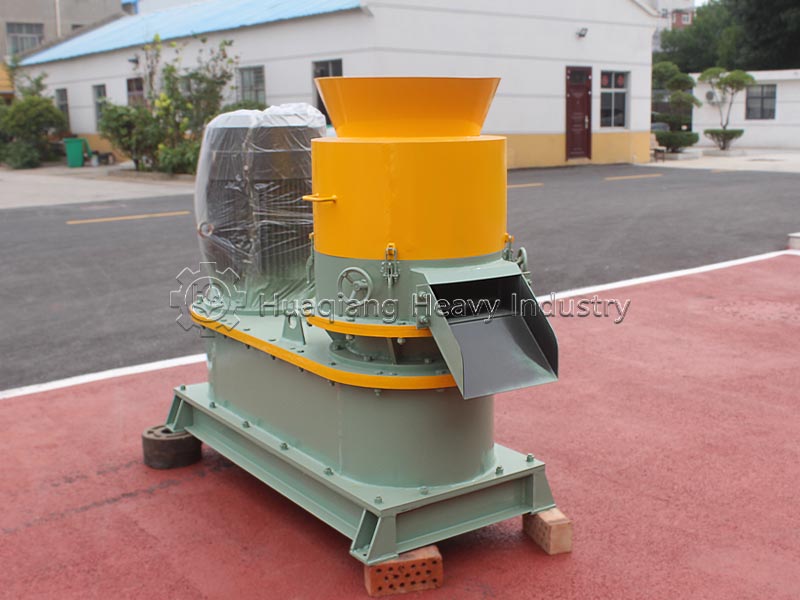
Rotary drum granulators are the “efficiency king” for large-scale production. They use rotating drums to tumble and bind materials into granules, offering wide adaptability. They can process various raw materials such as organic fertilizers and compound fertilizers, can operate continuously for 24 hours, have stable production capacity, and produce uniform granules, making them the preferred choice for granulating mixed materials.
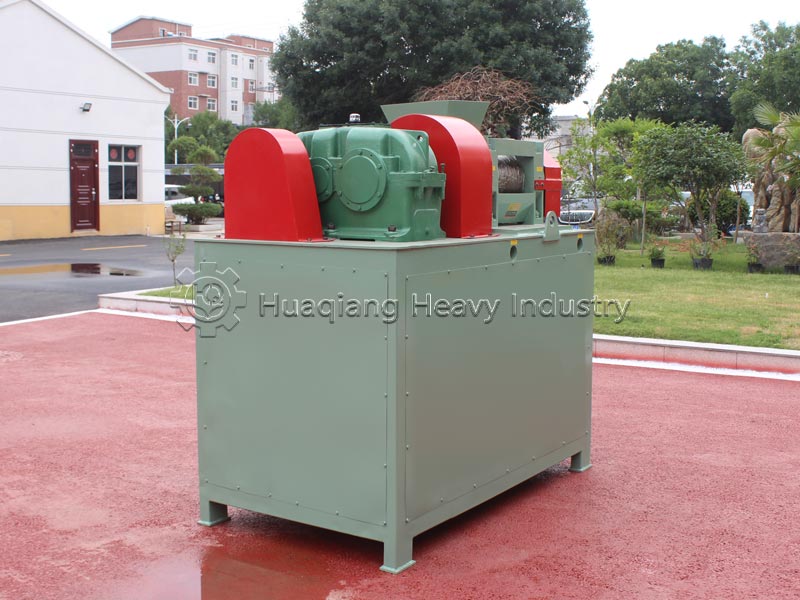

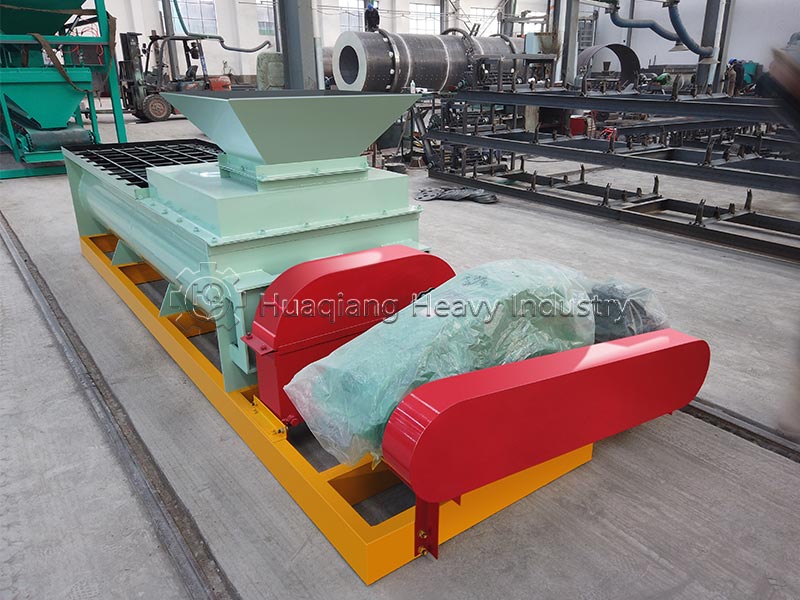
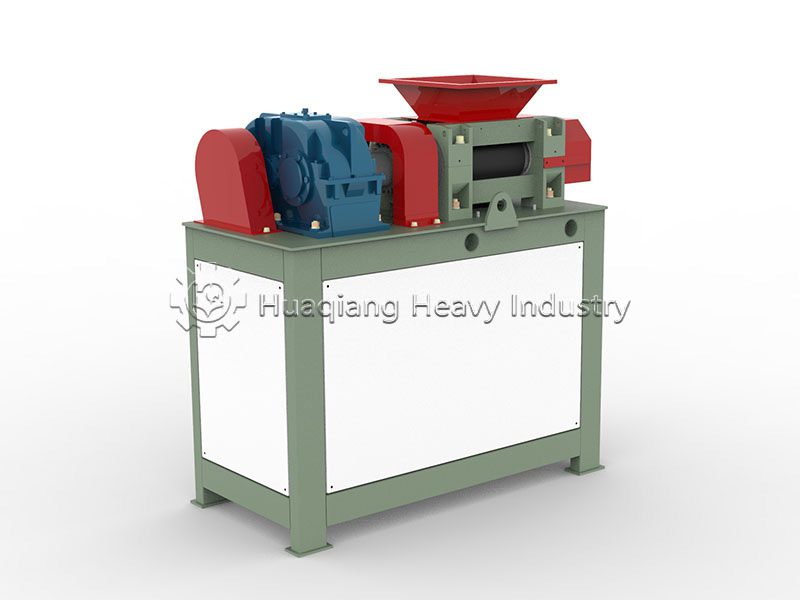
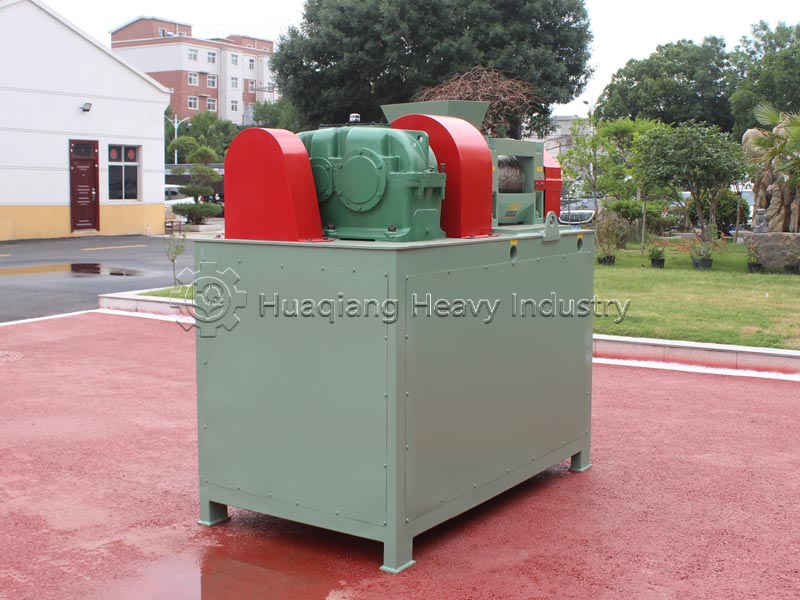
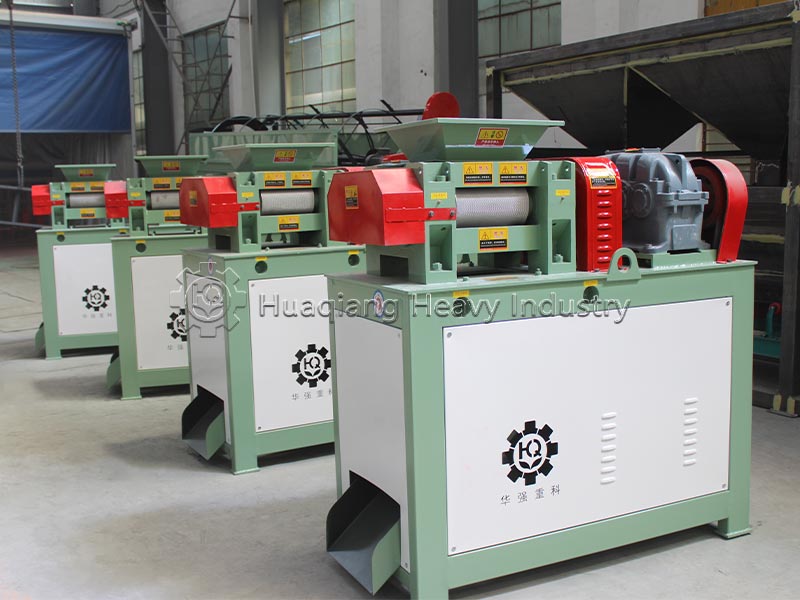
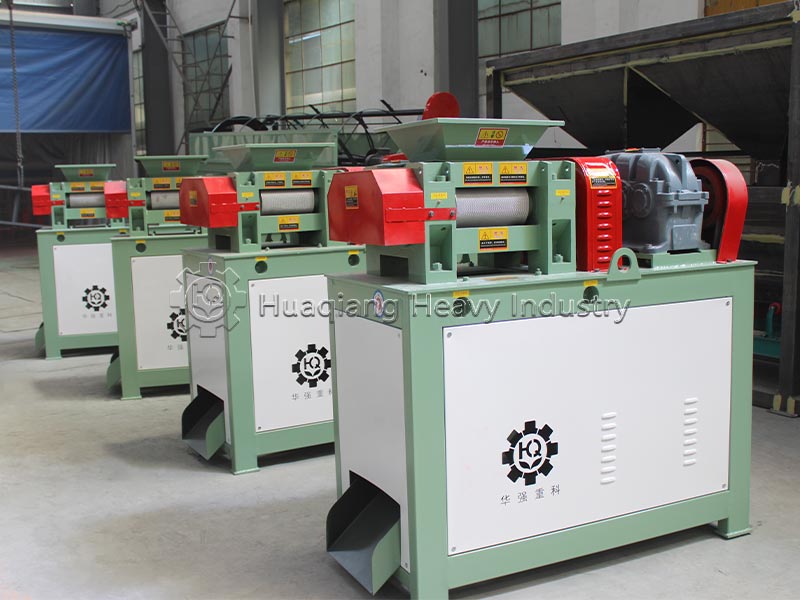
Double roller press granulators are the “hardcore choice” for dry granulation. They use physical extrusion molding, eliminating the need for large amounts of binders and high-temperature drying, resulting in low energy consumption and high granulation rate. The finished granules have high hardness and are not easily hygroscopic, suitable for dry materials and high-fiber raw materials. Operation and maintenance are convenient, solving the pain point of excessive dust in traditional granulation.
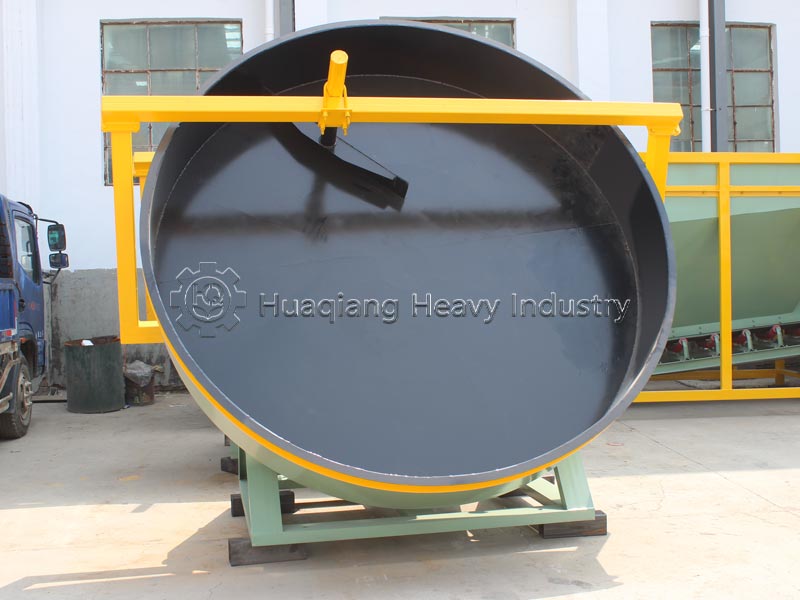
Disc granulators are “precision experts” in flexible production. They use a tilting, rotating disc to roll and shape materials, with adjustable parameters for precise control over particle size and roundness. Suitable for wet materials, they require low investment, are easy to maintain, and are ideal for small to medium-scale production, especially for fruit and vegetable fertilizers where high-quality granules are required.
In summary, there is no inherent superiority or inferiority among the three types of granulators. Rotary drum granulators prioritize high-efficiency mass production, roller granulators prioritize dry, energy-saving processes, and disc granulators prioritize flexibility and precision. Choosing the right type based on raw material requirements, production capacity, and finished product needs will maximize the equipment’s value.