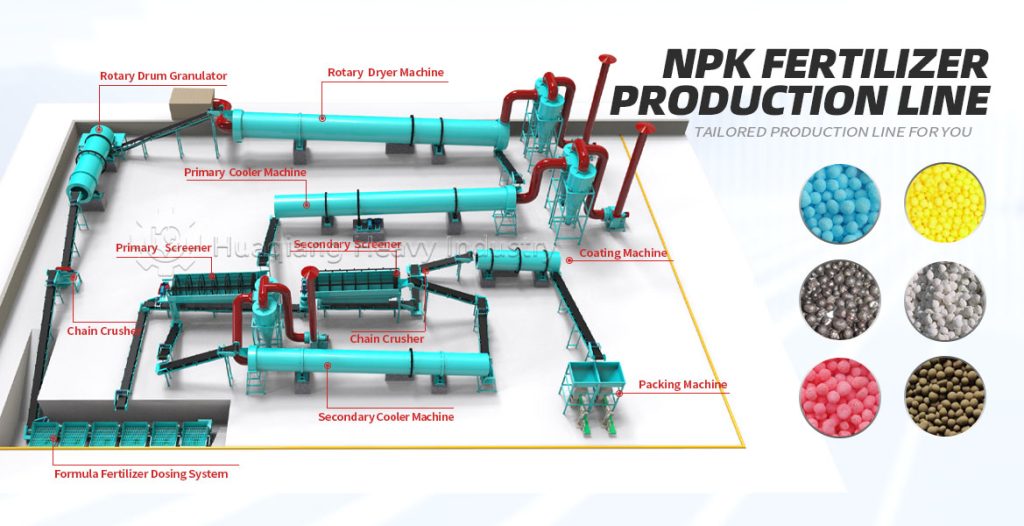
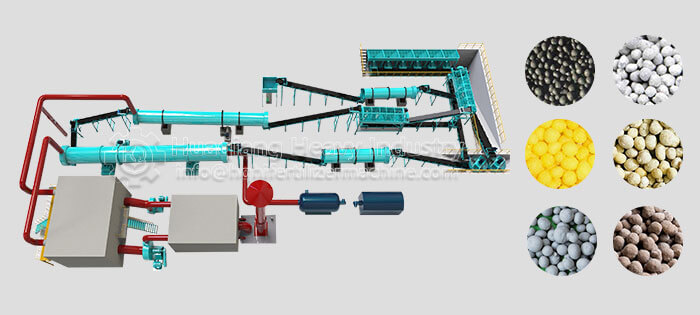
How to produce high-quality water-soluble NPK compound fertilizer?
Water-soluble NPK compound fertilizer is fast-dissolving, easily absorbed, and has a high utilization rate, making it suitable for intensive farming. Producing high-quality products requires full-process control of the NPK fertilizer production line, combined with optimized molding using a fertilizer granulator. From raw materials to finished products, each step is carefully controlled to ensure high purity, rapid dissolution, and balanced nutrients.
Step 1: Strict Raw Material Quality Control: Select high-purity, easily soluble raw materials. For nitrogen, choose urea or ammonium nitrate; for phosphorus, choose monoammonium phosphate; and for potassium, choose potassium chloride or potassium sulfate. Purity must reach 98% or higher to eliminate insoluble impurities that could affect dissolution.
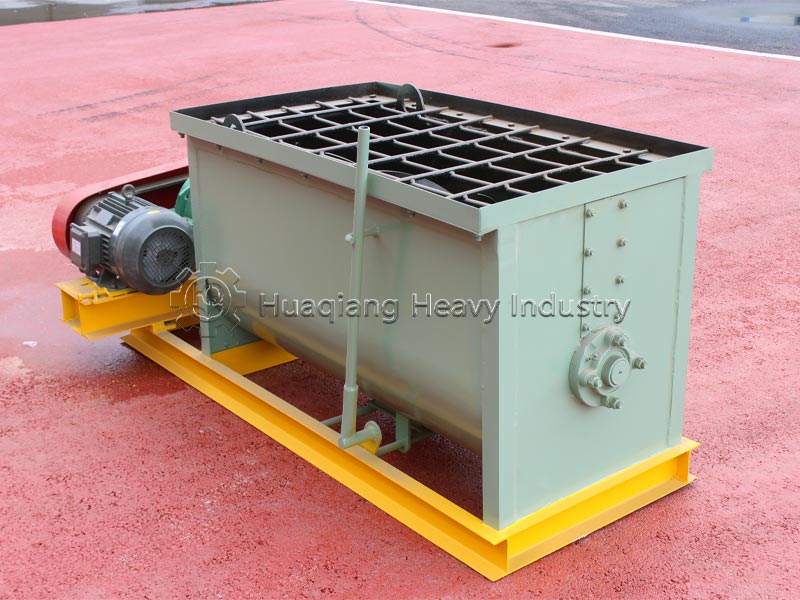
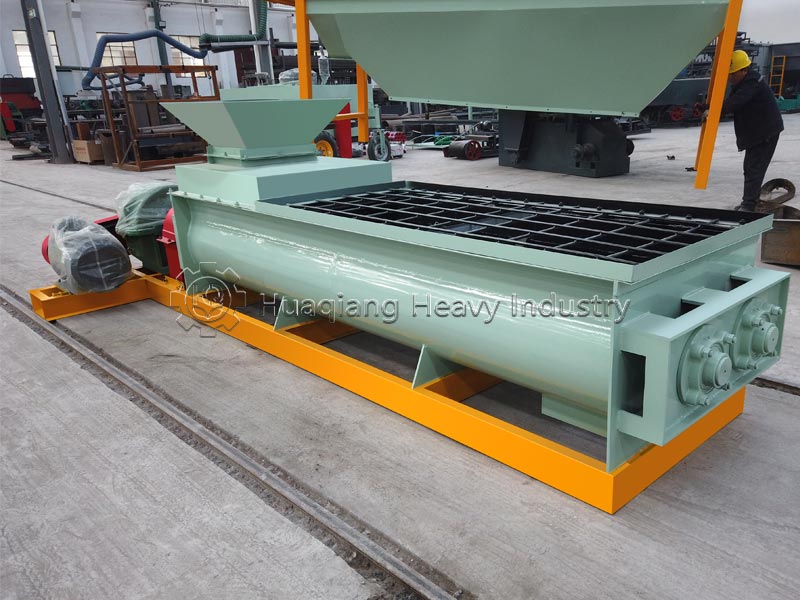
Step 2: Scientific Formulation: Precisely formulate the nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium ratio according to the needs of the crop and soil, adding appropriate amounts of micronutrients. Use a fertilizer mixer to thoroughly mix the fertilizer to ensure uniform nutrient distribution and avoid nutrient imbalance.
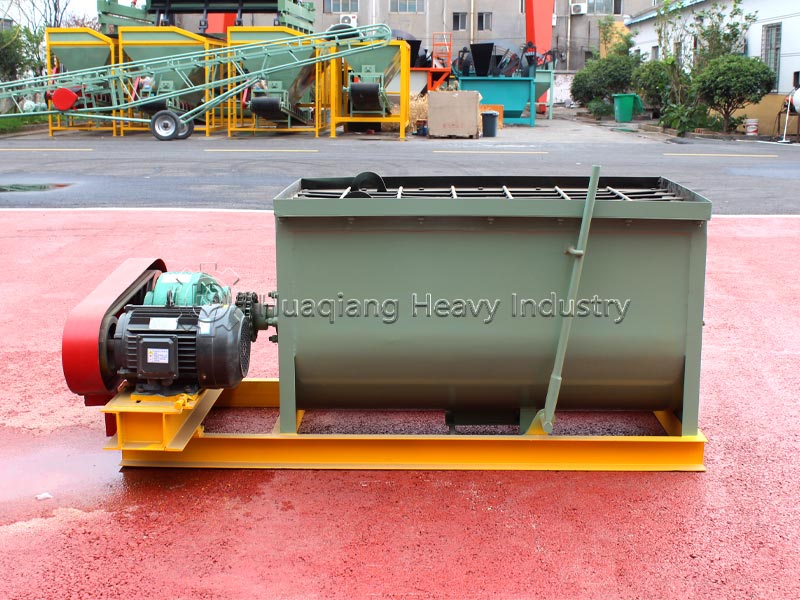

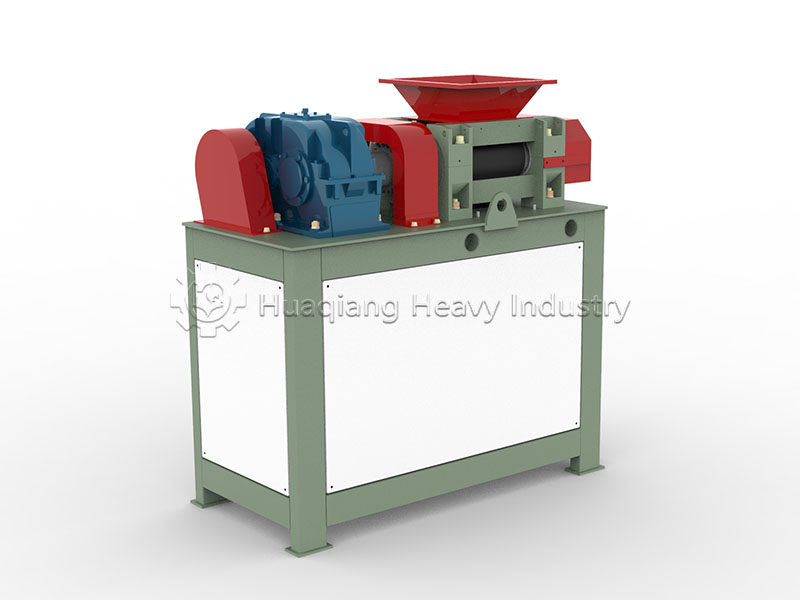
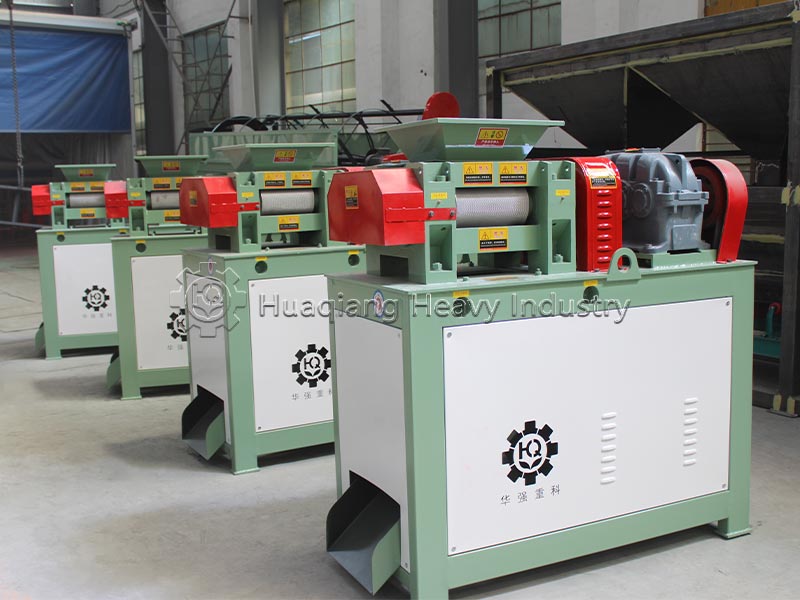
Step 3: Process Optimization: Advanced mixing and drying processes are employed in the NPK fertilizer production line, combined with fertilizer granulator to control granule uniformity, strictly control drying temperature to prevent nutrient loss, and maintain a clean production environment.
Step 4: Rigorous Testing: Finished products must be tested for solubility, nutrient content, and pH value to ensure no sedimentation, nutrient compliance, and crop suitability. Substandard products are strictly prohibited from leaving the factory.
In summary, by relying on the NPK fertilizer production line management and utilizing fertilizer granulation machines, and controlling the four key aspects of raw materials, formulation, process, and testing, high-quality water-soluble NPK compound fertilizer can be produced.