How long does it take for an organic fertilizer turning machine to ferment fertilizer
The fermentation time of organic fertilizer compost machine is affected by various factors, mainly including the type of raw materials, initial conditions (such as temperature and humidity), microbial activity, and turnover frequency. The following is a general time frame for using an organic fertilizer compost turning machine to ferment fertilizers: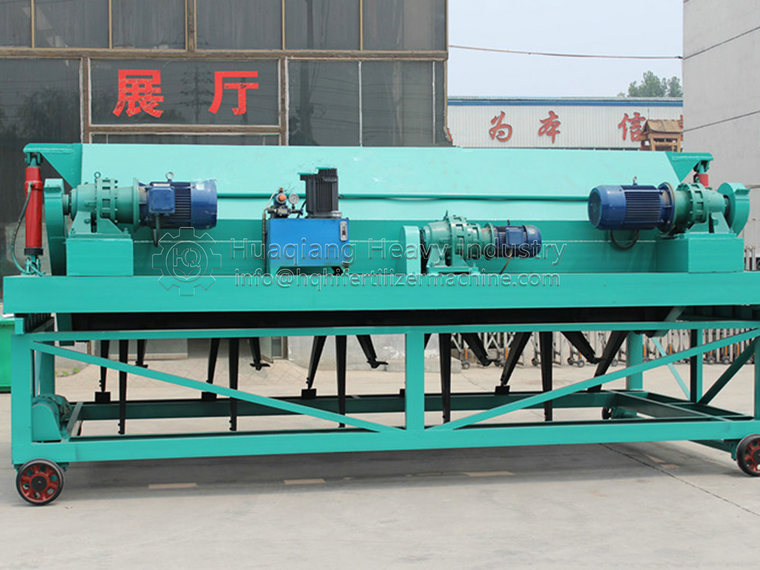
Raw material preparation stage: Firstly, organic raw materials (such as sheep manure, chicken manure, or other livestock manure) are mixed with other auxiliary materials (such as straw, rice straw, sawdust, etc.), and the appropriate carbon nitrogen ratio (C/N ratio) and moisture content are adjusted to create a favorable environment for microbial activity. The preparation time depends on the specific situation, mainly to ensure that the raw material is in a suitable state for fermentation.
Initial fermentation stage:
Temperature rise period: After the raw materials are stacked, as microorganisms become active, the temperature gradually rises, usually reaching a high temperature of 50-60 ℃ within 1-3 days. This is an important period for killing potential pathogens and seeds.
Continuous high temperature period: Once high temperature is reached, it is necessary to maintain this temperature for at least 5-7 days, sometimes up to two weeks, to ensure that all raw materials are fully decomposed and disinfected.
Flipping and cooling: Throughout the fermentation process, it is necessary to regularly use an organic fertilizer flipping machine to flip the compost, introduce new oxygen, adjust temperature and humidity, prevent local overheating, and help maintain optimal fermentation conditions. Generally, the pile is flipped every 3-5 days, and the specific interval can be flexibly adjusted according to the temperature monitoring results.
Maturity stage: When the temperature of compost begins to decrease, it indicates that most of the easily decomposable organic matter has been consumed and entered the maturity stage. At this point, the color of the compost becomes darker, the texture is looser, and there is no obvious odor. This usually occurs 2-4 weeks after fermentation begins, but full maturity may take several months to six months, depending on the composition of the raw materials and environmental conditions.
In general, the process of using an organic fertilizer turning machine to ferment fertilizers from raw material preparation to initial fermentation and final maturity takes approximately 4 weeks to several months. In order to achieve the most ideal fermentation effect, it is recommended to closely monitor the various parameters of compost, adjust strategies in a timely manner, and ensure a smooth transition at each stage. Note that different types of organic materials may have different fermentation characteristics, so adjustments should be made according to specific situations in practical operations.


.jpg)
.jpg)


