Guidelines for large-scale production of bio-organic fertilizer: Key to high-efficiency mass production
The core of large-scale bio-organic fertilizer production is achieving “resource utilization of raw materials, standardized processes, mechanized equipment, and controllable quality.” This requires relying on complete sets of equipment and scientific processes, balancing mass production efficiency and fertilizer activity. The core processes and key points are as follows:
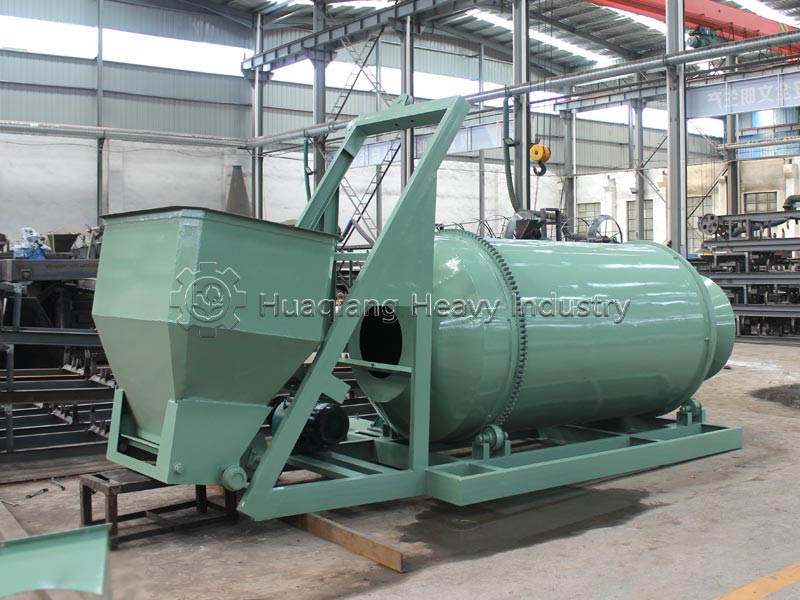
Step 1: Raw Material Pre-treatment and Proportioning: Collect livestock and poultry manure, crop straw, and other raw materials in batches. After crushing and screening to remove impurities, the materials are precisely mixed using a double axis paddle mixer according to a carbon-nitrogen ratio of 25-30:1 and a moisture content of 55%-60%, laying a solid foundation for microbial fermentation.
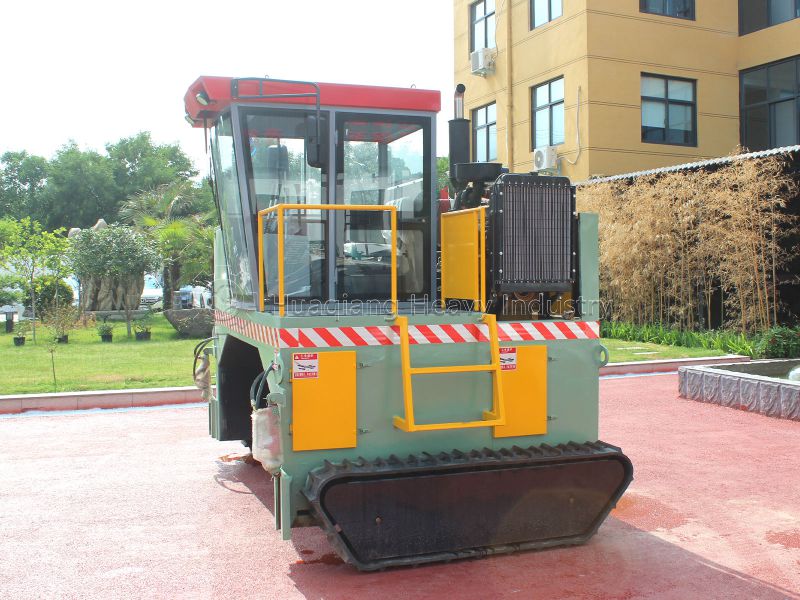
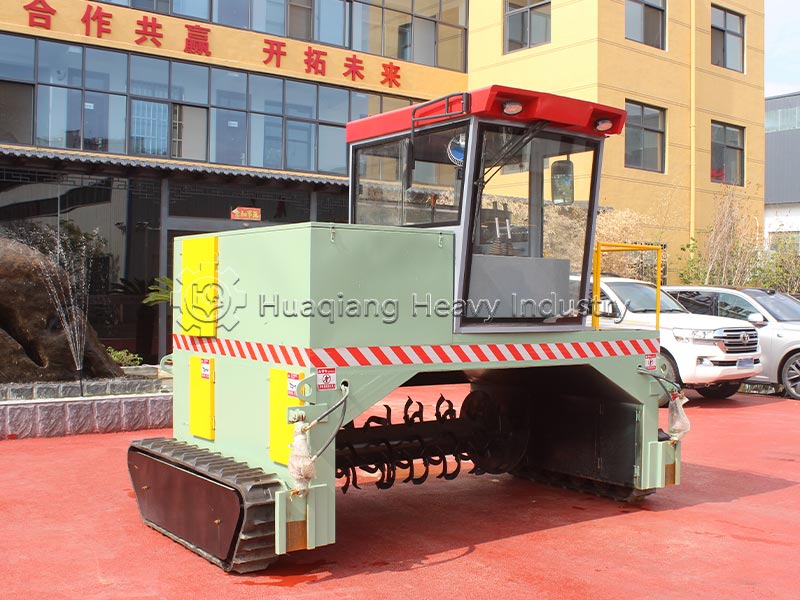
Step 2: Microbial Activation and High-Temperature Fermentation: Select high-efficiency microbial strains such as Bacillus subtilis, activate and expand them, and then mix them into the raw materials. Regular turning is performed using a compost turning machine, controlling the temperature at 55-65℃ and the pH value at 6.5-7.5. Fermentation takes 7-15 days to ensure thorough decomposition, kill pathogens, and preserve microbial activity. This is the core of the production process.
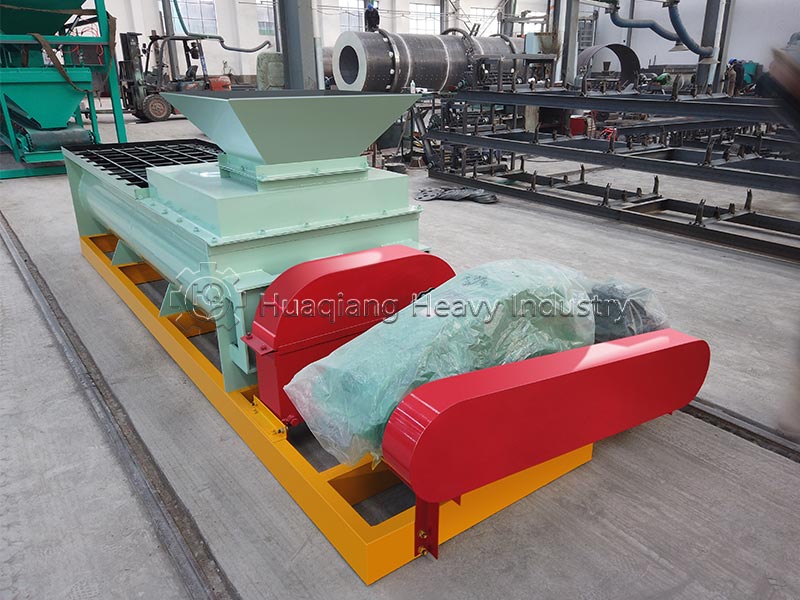

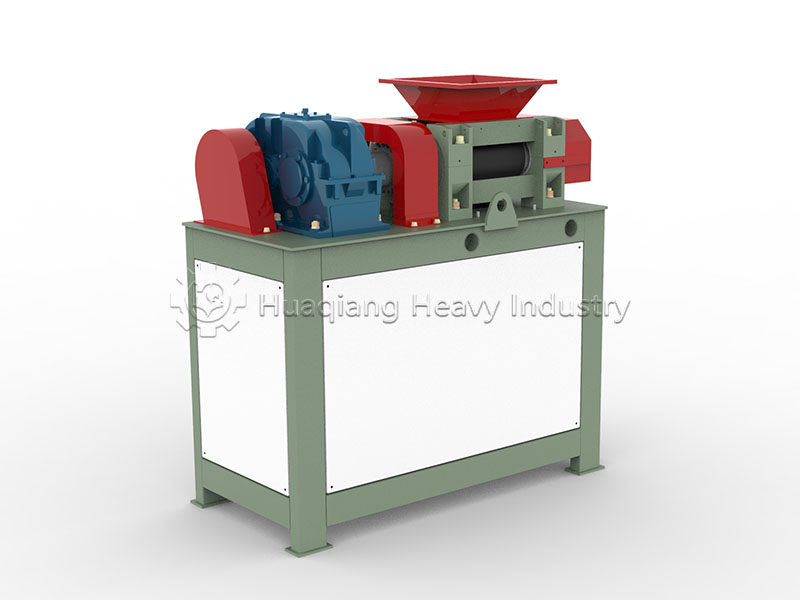
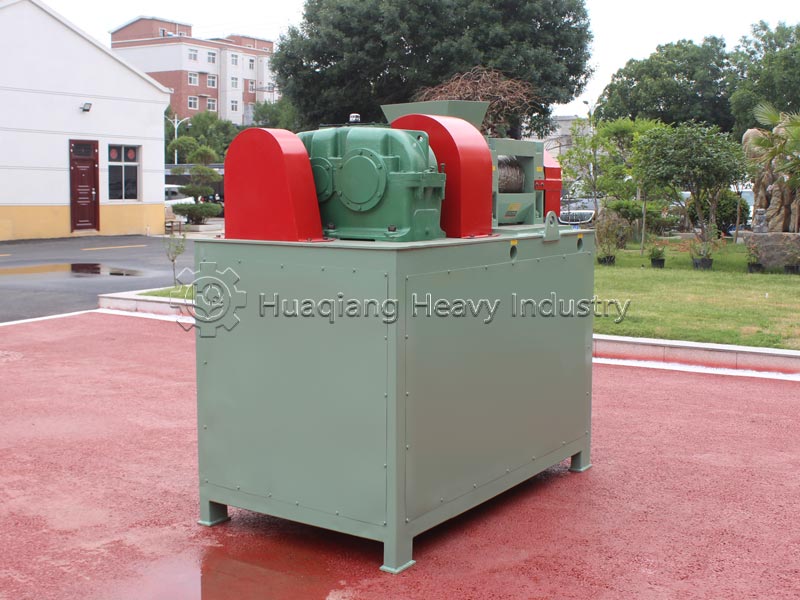
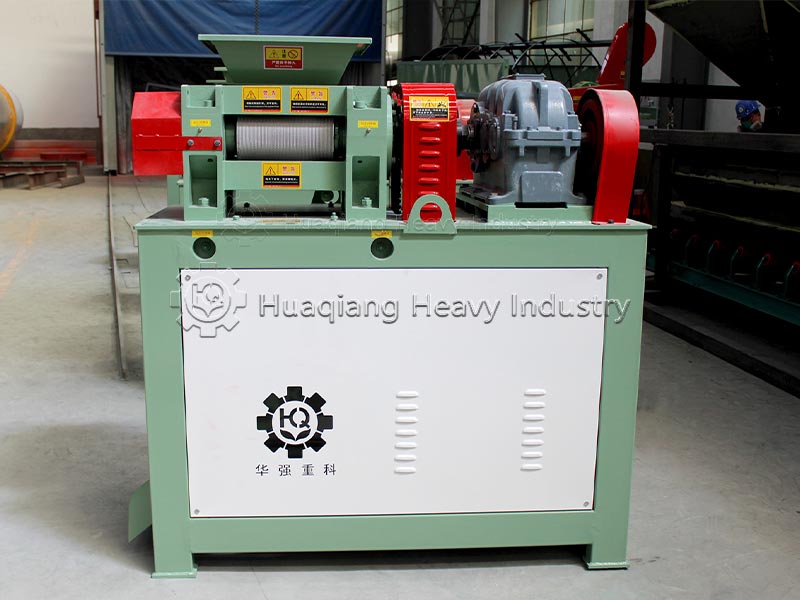
Step 3: Post-treatment and Granulation: The fermented material is dried at low temperature (moisture content ≤20%), crushed, and screened. Granulation is then performed using a double roller press granulator, balancing efficiency and microbial activity while avoiding high-temperature damage.
Step 4: Testing and Storage: The finished product is tested for indicators such as organic matter and effective viable bacteria count. After meeting the standards, it is packaged and stored. Storage requires ventilation, dryness, and protection from light and moisture. The entire process relies on a complete set of bio-organic fertilizer equipment to achieve continuous mass production.
In summary, the key to large-scale production is precise raw material proportioning, controllable fermentation, and coordinated equipment, ensuring both mass production and fertilizer quality, contributing to green and circular development in agriculture.