Methods for breaking up clumped organic fertilizer: Simple, efficient, and waste-free
Organic fertilizers tend to clump due to damp storage or prolonged stacking. While this doesn’t affect nutrient content, it hinders even application, leads to waste, and can cause problems for subsequent use of organic fertilizer production equipment. Breaking up clumps requires choosing a simple method based on the hardness of the clumps and the scale of use to quickly restore the fertilizer to a loose state.
For small-scale planting or home use, manual methods are sufficient. For softer clumps, simply rub them with your hands or crush them with a wooden stick, then sift to remove impurities. For harder clumps, spread them out to dry for 1-2 days to reduce moisture, then filter with a sieve and manually crush the hard clumps. This is convenient and cost-effective.
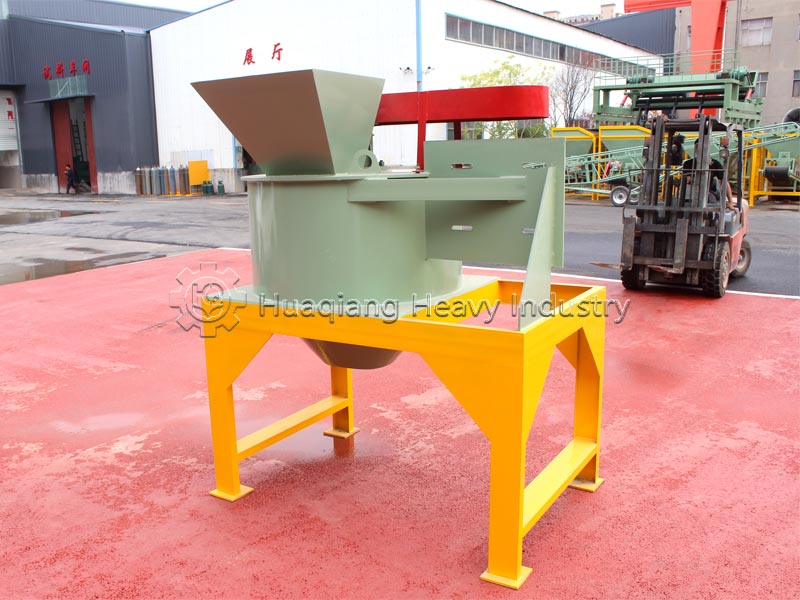

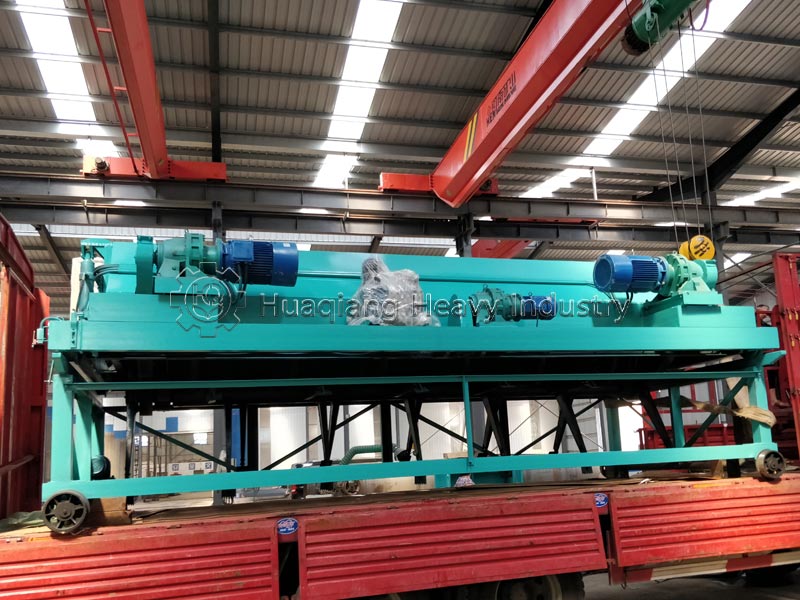
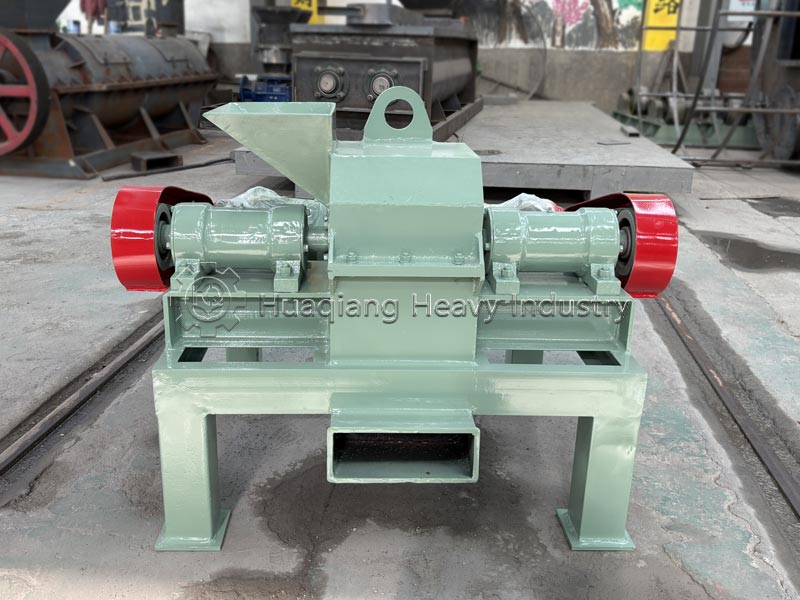
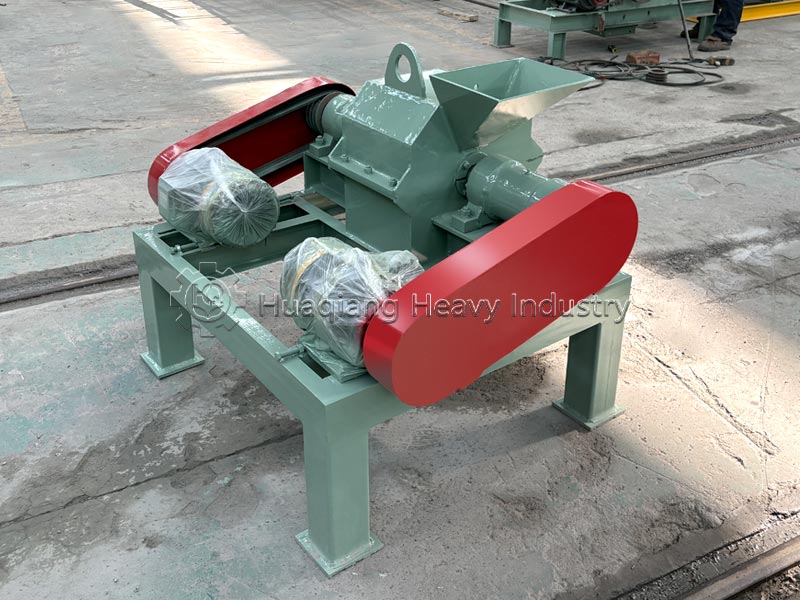
For medium-scale processing or large-scale field planting, tools can be used. Use a shovel to turn and break up the clumps, or use a small fertilizer crusher for quick crushing. Sifting ensures uniform particle size, suitable for mechanized fertilization, and can also serve as an auxiliary tool for organic fertilizer production equipment.
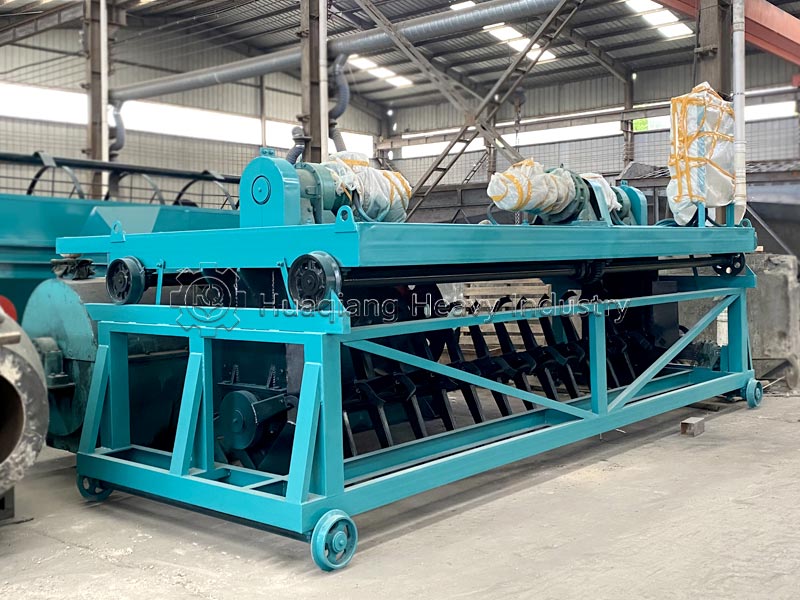
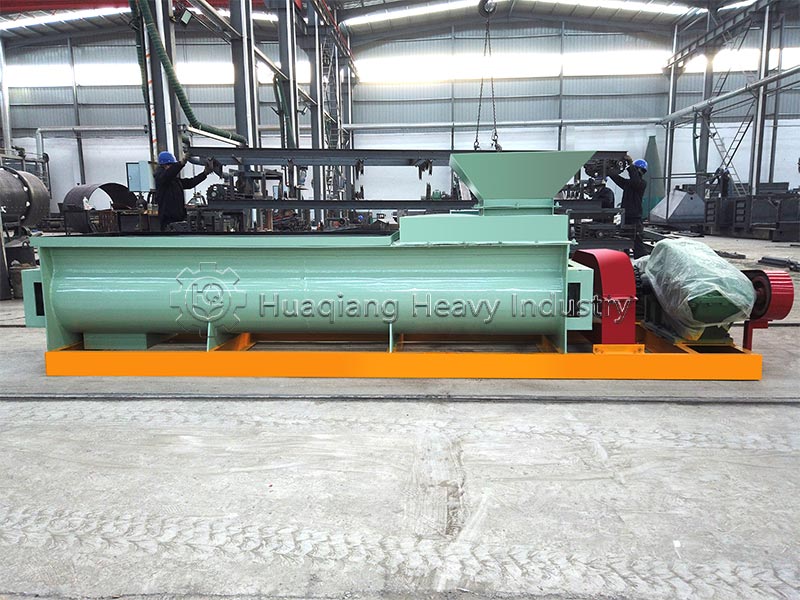
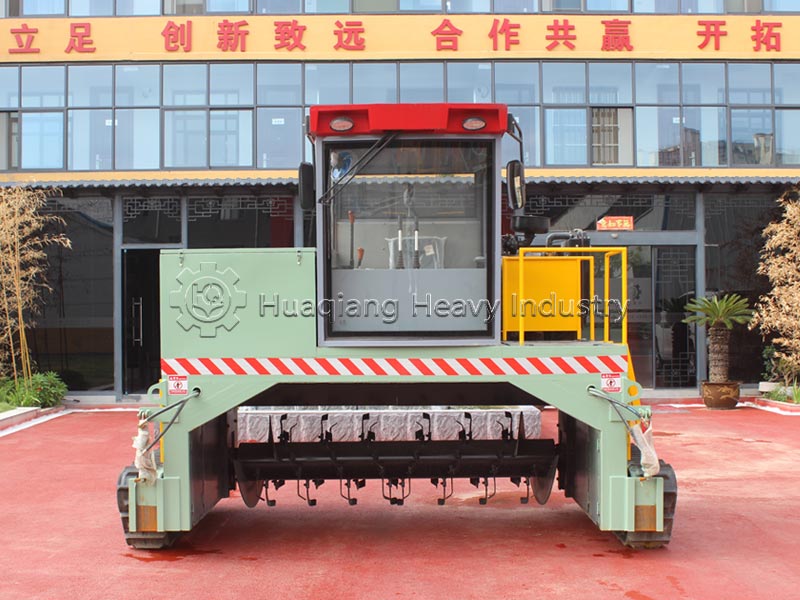
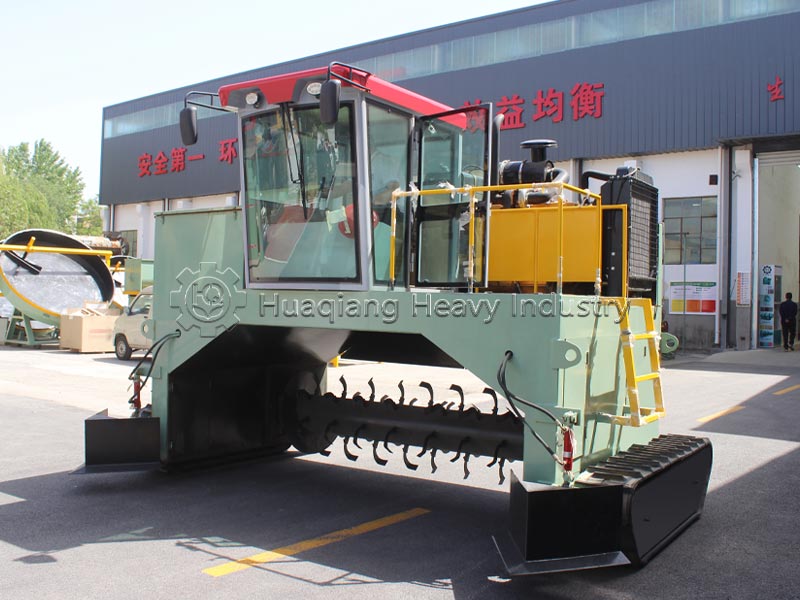
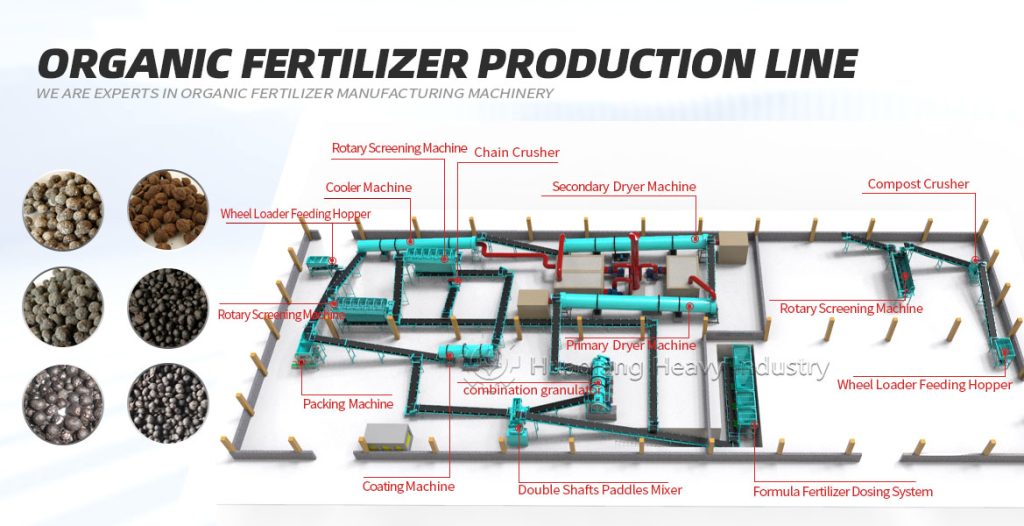
In large-scale production, clumped organic fertilizer can be fed into the corresponding section of the organic fertilizer production line, using the fertilizer crusher and screening equipment to break up the clumps while controlling humidity to prevent re-clumping, ensuring both efficiency and uniform product quality.Additional reminder: After breaking up the clumps, the fertilizer should be sealed promptly and stored in a dry, well-ventilated place to reduce re-clumping and maximize nutrient utilization.