In the selection of raw materials for bio-organic fertilizer production lines, cow dung is one of the core raw materials, and its quality directly determines the granulation effect and product quality of the organic fertilizer. Not all cow dung is suitable for granulation; strict selection from multiple dimensions is necessary to ensure the smooth operation of the granulation process in the bio-organic fertilizer production line and that the product meets the standards.
First, prioritize fresh cow dung from healthy beef or dairy cattle. The manure of healthy cows is free from pathogens and insect eggs, and the organic matter, nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium nutrients are fully preserved. It is the core source of nutrients for bio-organic fertilizer and lays a solid foundation for subsequent stages of the bio-organic fertilizer production line. Avoid manure from sick cows or cows undergoing medication. This type of cow dung may contain residual pathogens or drug components, which not only affects the safety of the granulated organic fertilizer but may also cause abnormalities in the fermentation process of the bio-organic fertilizer equipment.
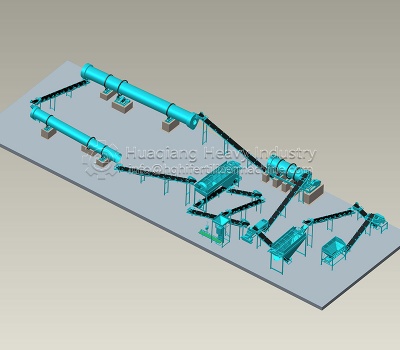
Secondly, control the degree of cow dung decomposition. Uncomposted raw cow dung should never be directly granulated. Raw cow dung will continue to ferment and heat up after granulation, easily leading to granule expansion and cracking, and may burn crop roots when applied. It is recommended to use fully composted cow dung, which is dark brown, odorless, and has a loose texture. The organic matter has been fully decomposed, which not only facilitates the formation of uniform granules but also improves the stability of the organic fertilizer’s effectiveness.
In addition, strictly control the impurity content of the cow dung. Cow dung used for granulation needs to be cleaned of impurities such as stones, plastics, metals, and weed roots beforehand to prevent damage to the granulation components of the bio-organic fertilizer equipment, affecting the granule formation rate and uniformity, and slowing down the overall efficiency of the bio-organic fertilizer production line. The moisture content should also be adjusted to 25%-35%. Too high a moisture content can cause sticking and clumping, leading to blockages in the bio-organic fertilizer equipment, while too low a moisture content makes granulation difficult. This can be adjusted by drying or adding auxiliary materials.