In today’s industrial production and agricultural development, the rotary drum granulator, as an efficient and reliable granulation equipment, is playing an increasingly important role. Through unique mechanical design and process principles, this equipment transforms powdered materials into uniform granules, providing high-quality product forms for various industries.
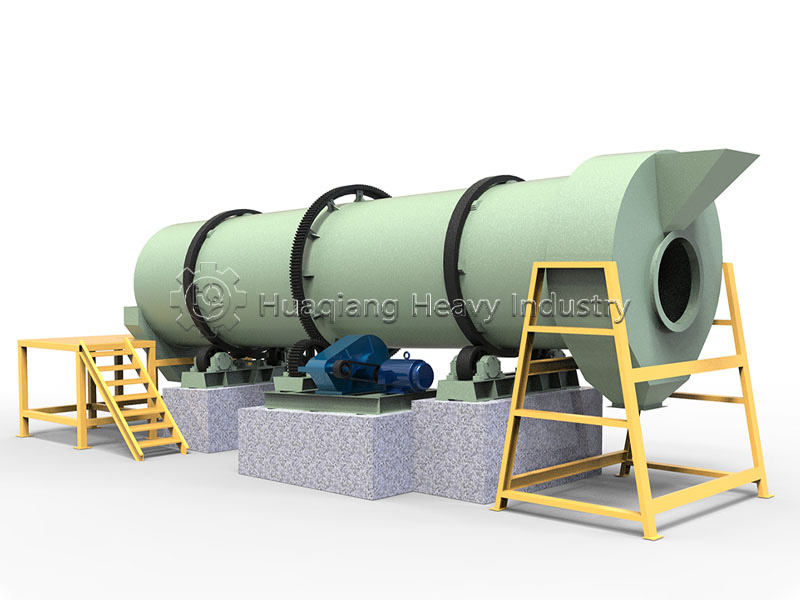

Working Principle and Basic Structure
The core of a rotary drum granulator is an inclined rotating cylinder. When mixed materials enter the cylinder, driven by an electric motor, the cylinder rotates uniformly at 5-20 rpm. Under the combined action of gravity, friction, and centrifugal force, materials continuously tumble and collide within the cylinder. Simultaneously, a spray device applies appropriate amounts of water or binder to the materials, moistening particle surfaces and causing them to adhere together, gradually aggregating into granules with certain strength and size. This wet granulation method is particularly suitable for processing various materials, capable of producing high-quality granules with good sphericity and moderate strength.
The rotary drum granulator not only features simple structure and easy operation but also possesses strong production capacity and wide material adaptability, making it the preferred granulation equipment in multiple industries such as fertilizers and chemicals.
Wide Application Across Multiple Fields
The application scope of rotary drum granulators is extremely broad. In the fertilizer field, it can produce various compound fertilizers, organic fertilizers, and inorganic fertilizers, mixing basic fertilizers such as nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium in certain proportions to produce fertilizer products meeting different crop and soil needs. In the chemical industry, this equipment can be used for granulating chemical raw materials like catalysts, pigments, and detergents, improving product fluidity, stability, and performance. Additionally, in metallurgical and building materials industries, rotary drum granulators also play important roles, usable for granulating metal ore powders and cement raw materials to improve material properties and enhance product quality and production efficiency.
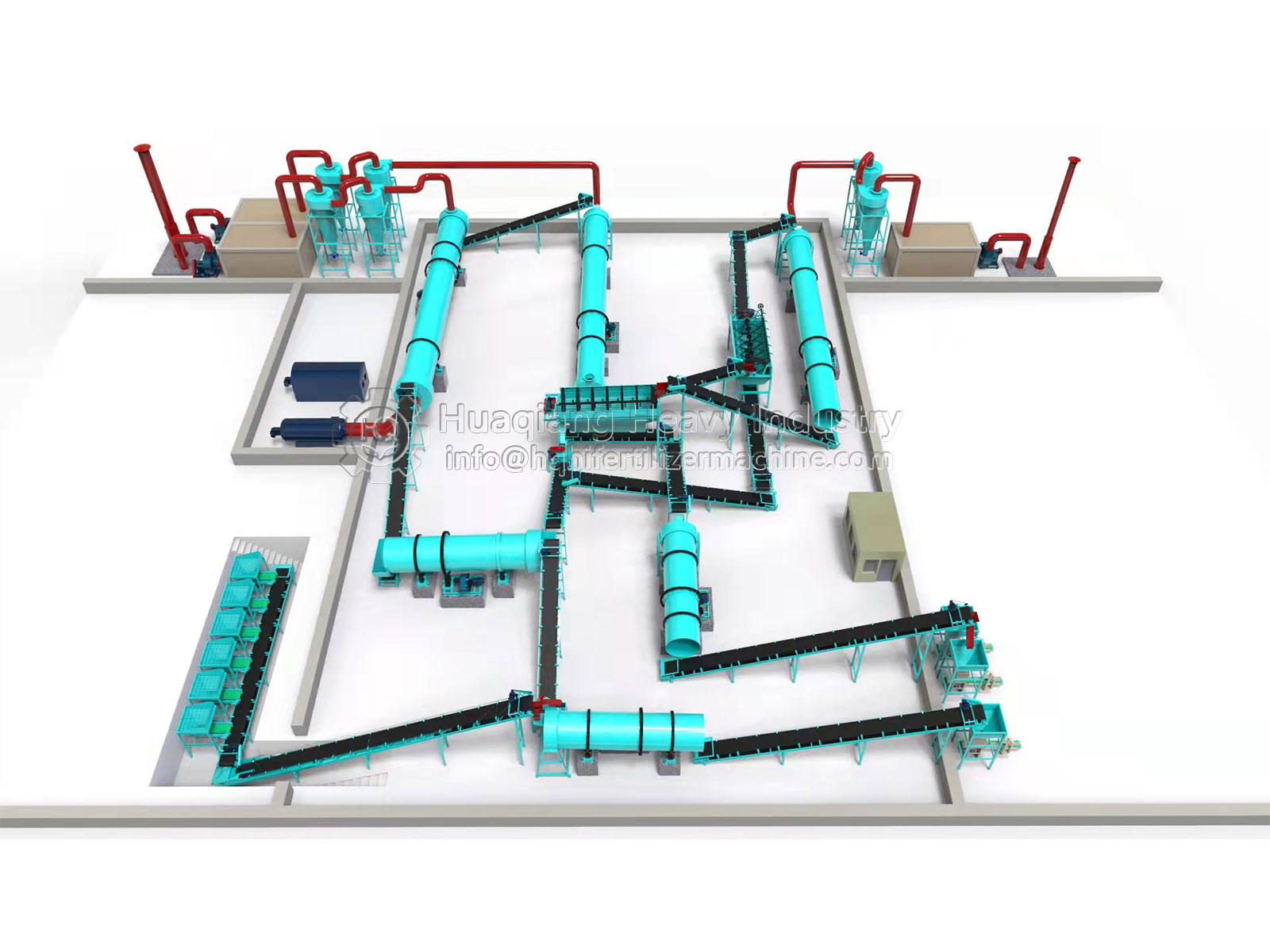
Systematic Fertilizer Production Process
Using rotary drum granulators for fertilizer manufacturing is a systematic process. First, raw materials require pretreatment including crushing, screening, and batching to ensure materials reach particle size and proportions suitable for granulation. Subsequently, uniformly mixed materials are fed into the rotary drum granulator, where under appropriate rotation speed and inclination angle, combined with water or binder spraying, granule formation is completed. Post-granulation products require post-processing steps such as drying, cooling, and screening before finally obtaining qualified fertilizer products. The entire process requires careful process control and equipment coordination to ensure stable quality of final products.
With continuous technological advancement and growing industrial demands, rotary drum granulators will continue to play important roles across various industries. Their characteristics of efficiency, stability, and strong adaptability make them indispensable key equipment in modern granulation technology, providing powerful technical support for global industrial development and agricultural production.
The Central Role of Drum Granulation in Modern Fertilizer Manufacturing
The rotary drum granulator, also commonly referred to as a drum granulator, is a cornerstone technology in the wet granulation segment of the npk manufacturing process. As a key component of a complete npk production line, this equipment efficiently transforms blended powders into uniform, spherical granules through a tumbling and layering mechanism. Its operation stands in contrast to dry granulation processes that rely on fertilizer granules compaction without added moisture.
The widespread adoption of rotary drum granulators underscores their efficiency and reliability for large-scale, continuous fertilizer production. Their ability to handle diverse raw material formulations and produce consistent, high-strength granules makes them an indispensable part of modern compound fertilizer manufacturing, supporting global agriculture with a steady supply of precisely formulated nutrients.