Opening new pathways in organic fertilizer production and environmental treatment
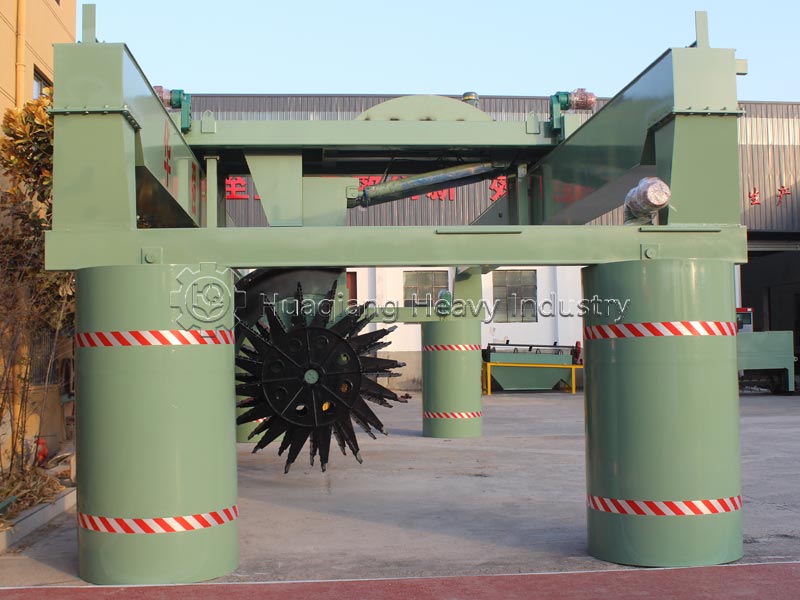
In the fields of organic fertilizer production, bioenergy development, and environmental treatment, a highly efficient piece of equipment is becoming the industry’s “new favorite”: the simple compost turning machine. This equipment is specifically designed for organic materials such as livestock and poultry manure, crop straw, and kitchen waste. Through aerobic fermentation technology, it easily achieves the resource utilization of organic waste.
Traditional organic material processing often faces problems such as low fermentation efficiency and high labor costs. The simple compost turning machine overcomes these challenges with its unique advantages. It features an automated operation design and is equipped with a PLC control system, allowing for precise control of movement, turning, and oxygen supply, reducing manual intervention. During operation, the equipment moves along the fermentation tank, turning the materials through a stacking mechanism. The oxygen supply system ensures sufficient oxygen, accelerating microbial activity and significantly improving fermentation efficiency, allowing organic materials to be quickly converted into high-quality organic fertilizer.
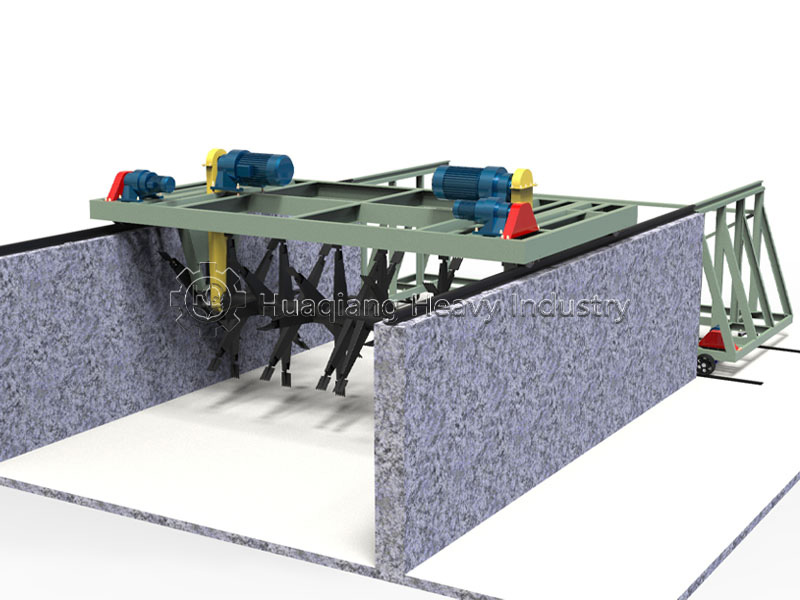

Furthermore, this equipment is highly adaptable and can meet the processing needs of different organic materials. Whether it’s batch processing on an organic fertilizer production line or waste conversion in environmental treatment projects, it can handle the task. As a professional manufacturer, we also provide complete organic fertilizer production line solutions, including NPK fertilizer production lines, disc granulation production lines, and other equipment, covering everything from material processing to finished product processing.
Today, environmental protection and resource recycling are becoming trends. The simple compost turning machine not only helps the agricultural sector produce green organic fertilizers but also promotes the reduction and resource utilization of organic waste, contributing to environmental protection.