Composting principles and process implementation
Composting is essentially a microbially driven aerobic decomposition process. Through the metabolism of microbial communities, organic waste such as livestock manure and crop residues are transformed into stable humus, achieving harmlessness and resource utilization. The core principle is to regulate environmental conditions to suit microbial activity.
The composting process progresses through three stages. The high-temperature phase is the core stage, where thermophilic bacteria rapidly decompose organic matter, raising the pile temperature to 55-65°C for several days to kill pathogens and insect eggs; in the cooling phase, mesophilic bacteria take over the decomposition of residual organic matter, and the pile temperature drops to around 40°C; in the maturation phase, microbial activity stabilizes, and the organic matter is transformed into loose, odorless humus.
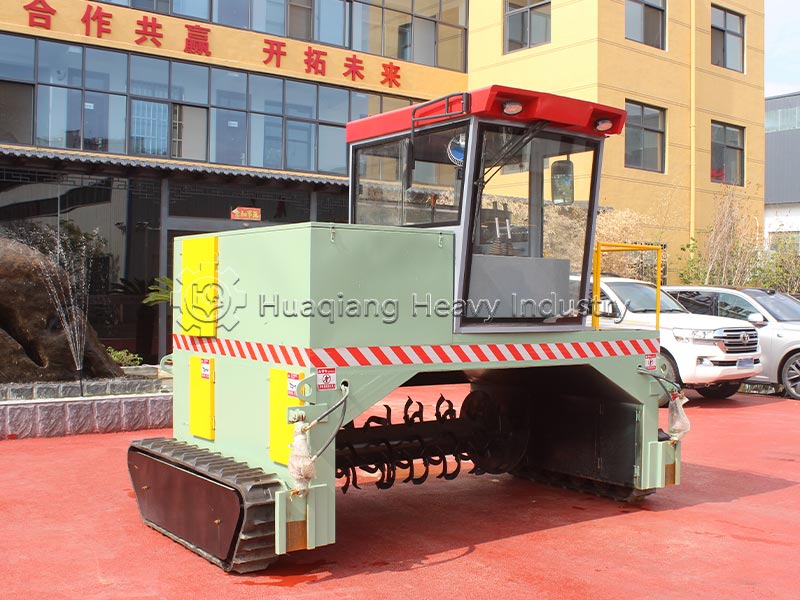

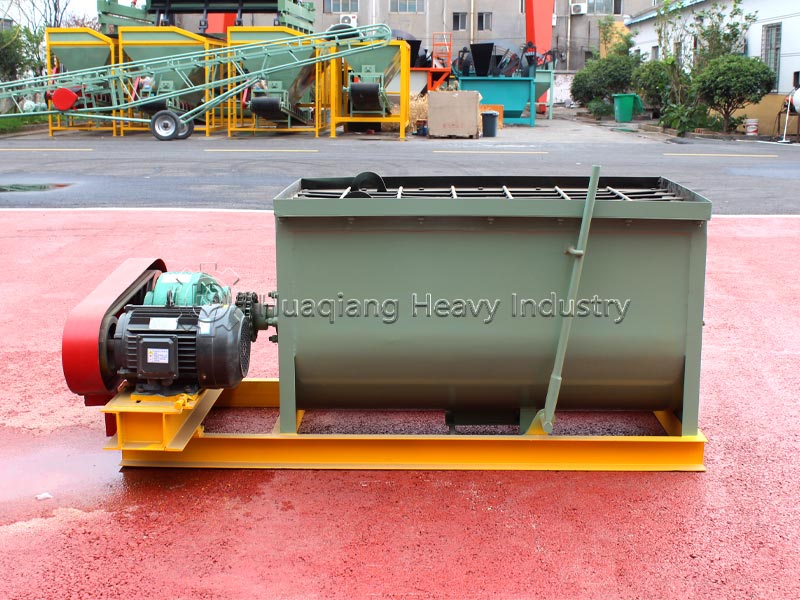
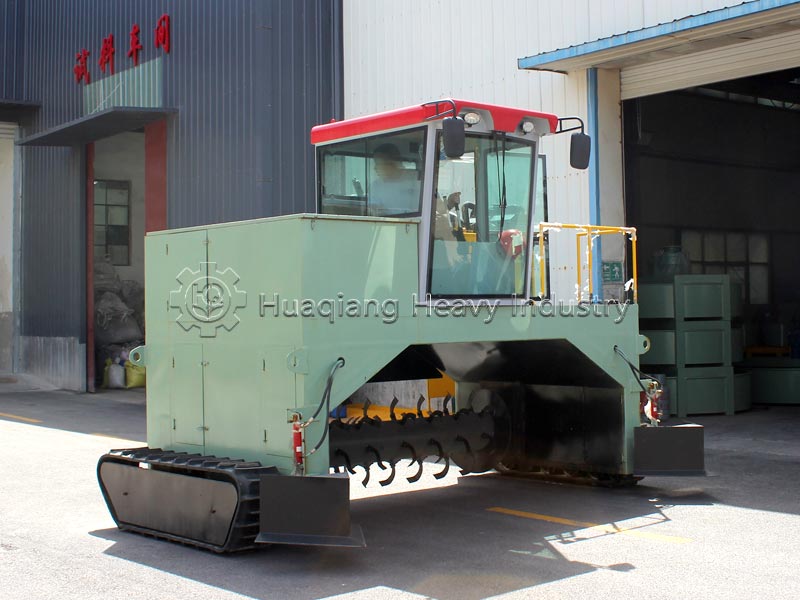
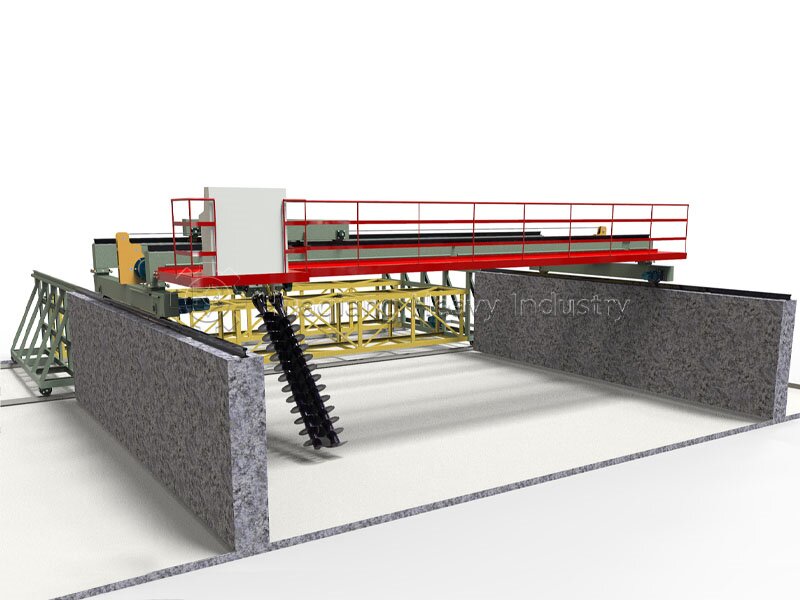
Process implementation requires controlling four key steps. First, raw material proportioning: mix carbon sources (straw, sawdust) and nitrogen sources (livestock manure) at a carbon-to-nitrogen ratio of 25:1-30:1, and adjust the moisture content to 55%-60% to provide a suitable environment for microorganisms. Second, piling: pile the materials into a pile 1.5-2 meters high to ensure aeration and prevent anaerobic fermentation.
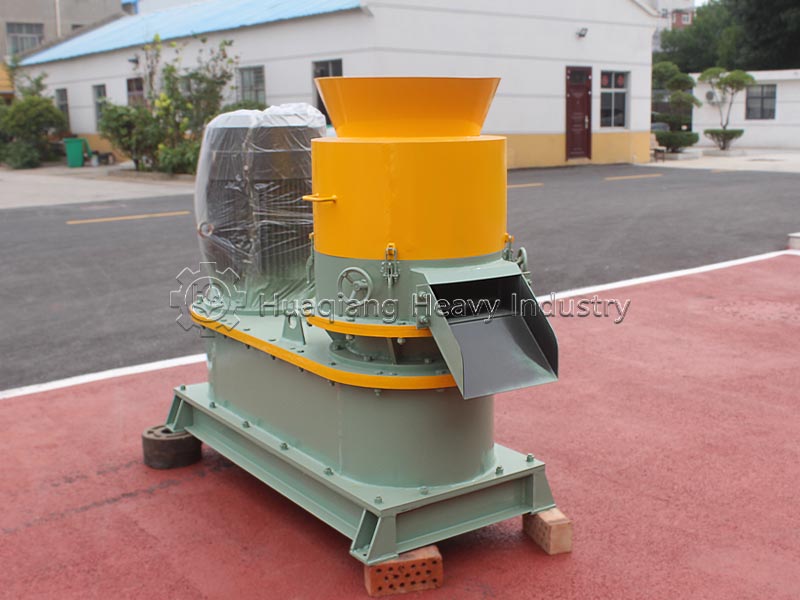
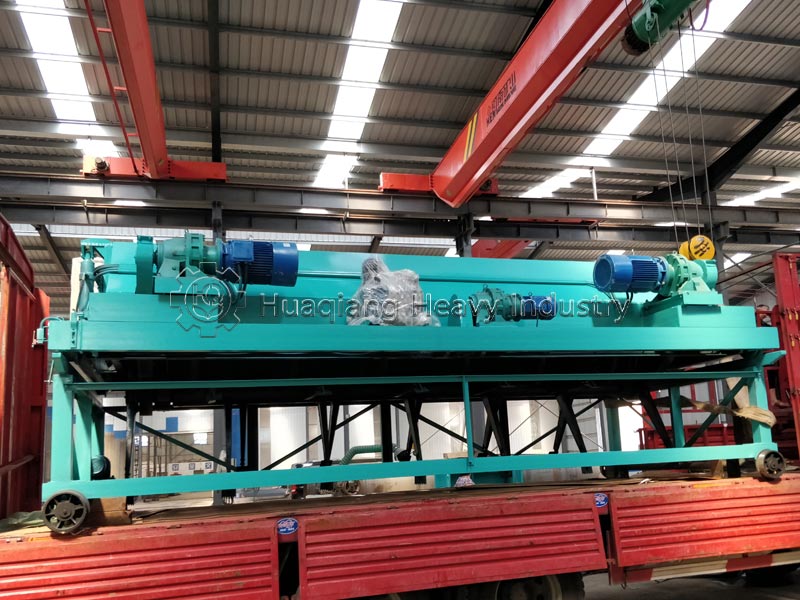
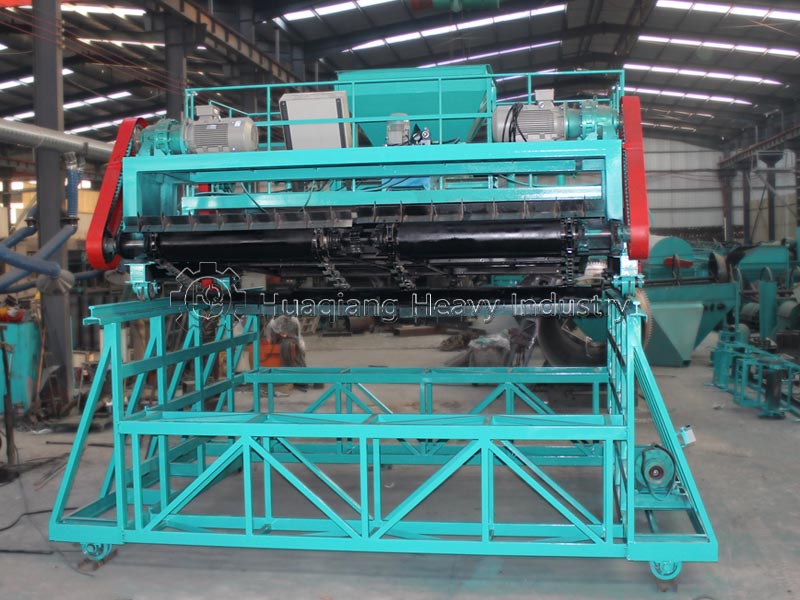
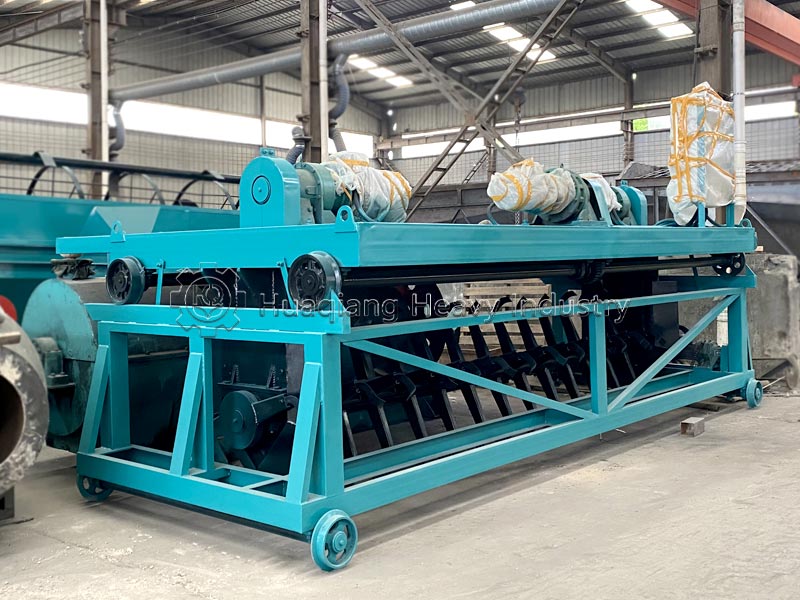
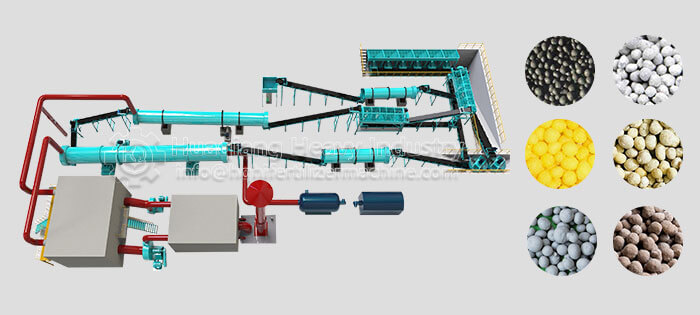
Third, turning and control: use a large wheel compost turning machine or windrow compost turning machine to regularly turn the pile to replenish oxygen and adjust temperature and humidity. During the high-temperature phase, turn the pile every 2-3 days; the interval can be extended during the cooling phase. Fourth, maturation judgment: when the pile temperature drops to ambient temperature, there is no odor, and the material is black and loose granules, the composting process is complete. The entire process does not require complex equipment; large-scale production can rely on organic fertilizer production lines for precise parameter control to improve efficiency and quality.