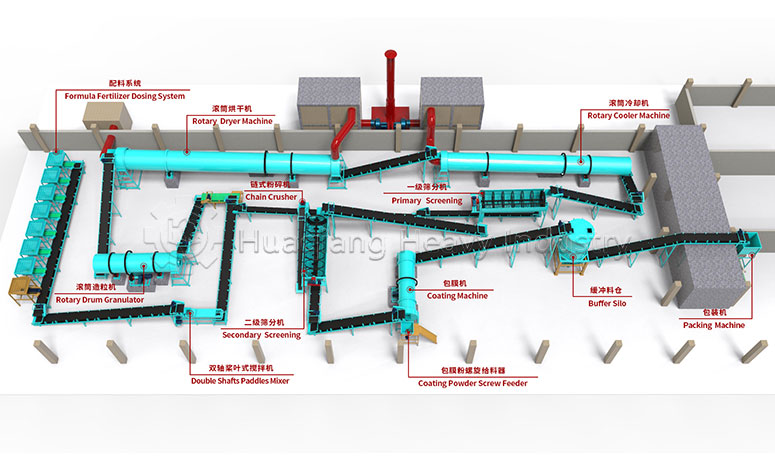
What are the core differences between blended fertilizers and compound fertilizers?
Blended fertilizers and compound fertilizers are often confused, but they differ significantly in core dimensions such as production process and nutrient uniformity. Precise differentiation is necessary when choosing between them, based on specific planting needs. The core difference lies in: compound fertilizers are “synthesized first, then formed,” while blended fertilizers are “formed first, then mixed.” This fundamental difference determines their fertilizer efficacy characteristics and applicable scenarios.
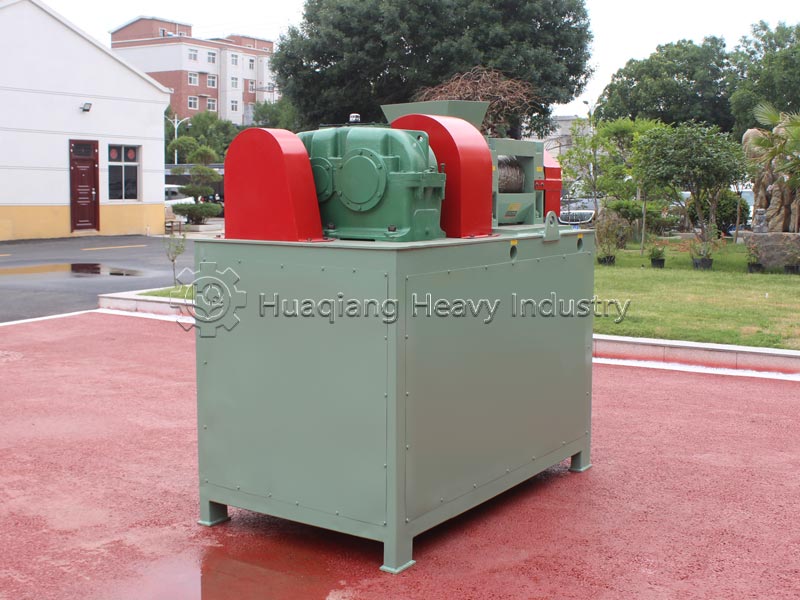
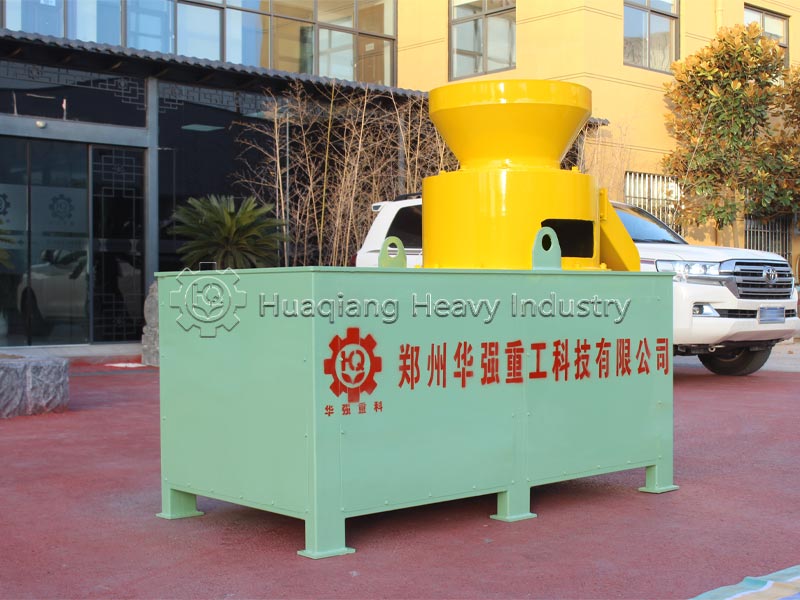
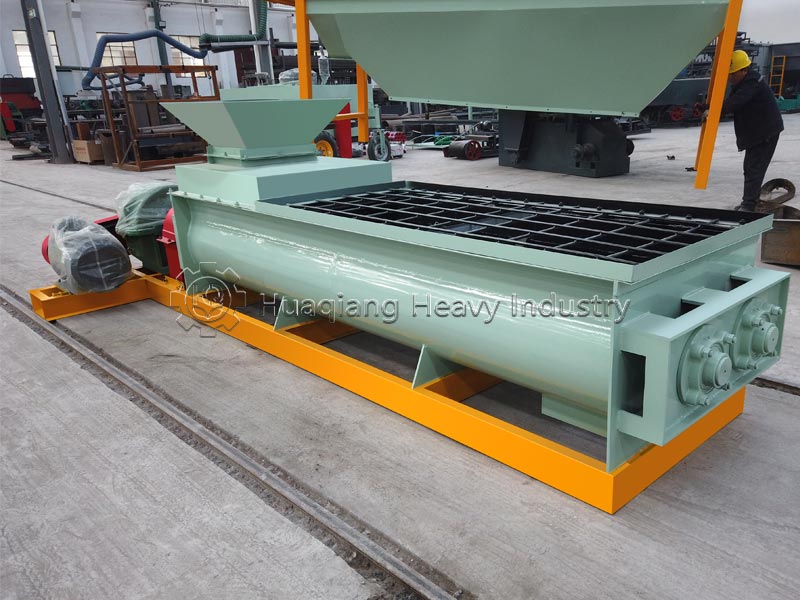
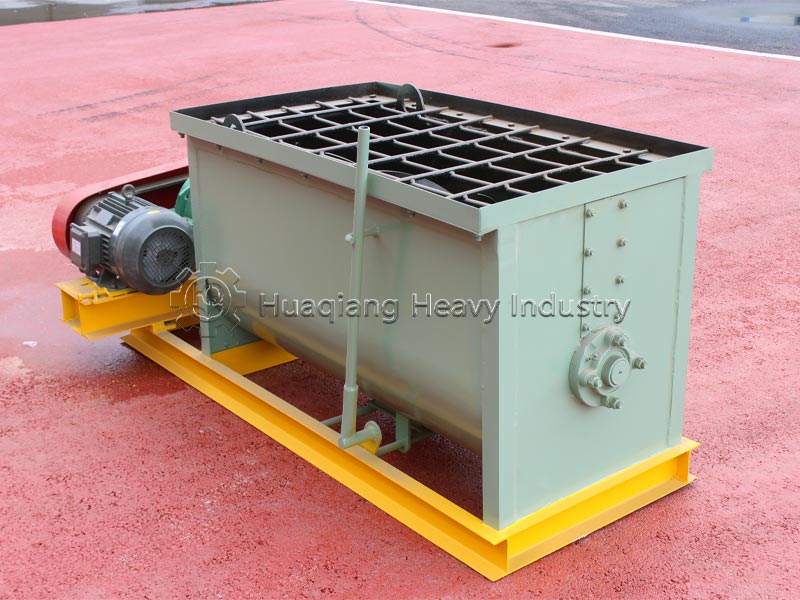
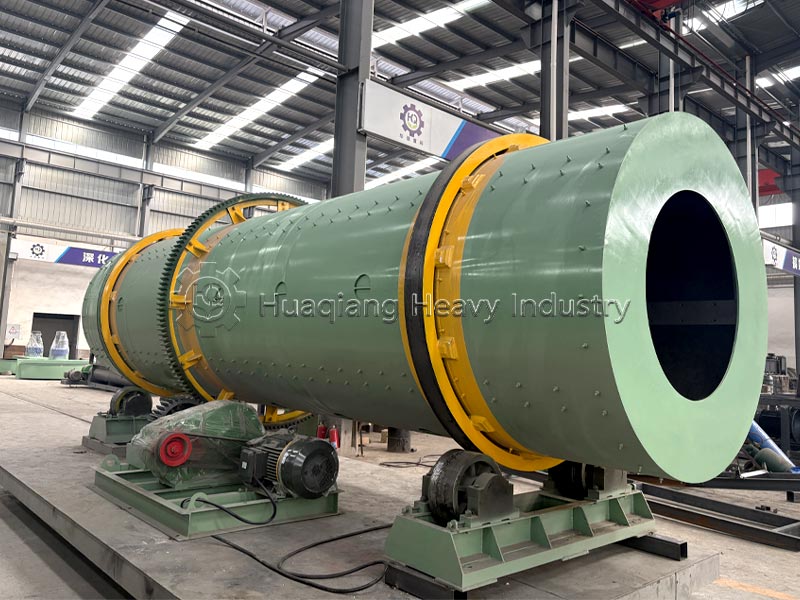
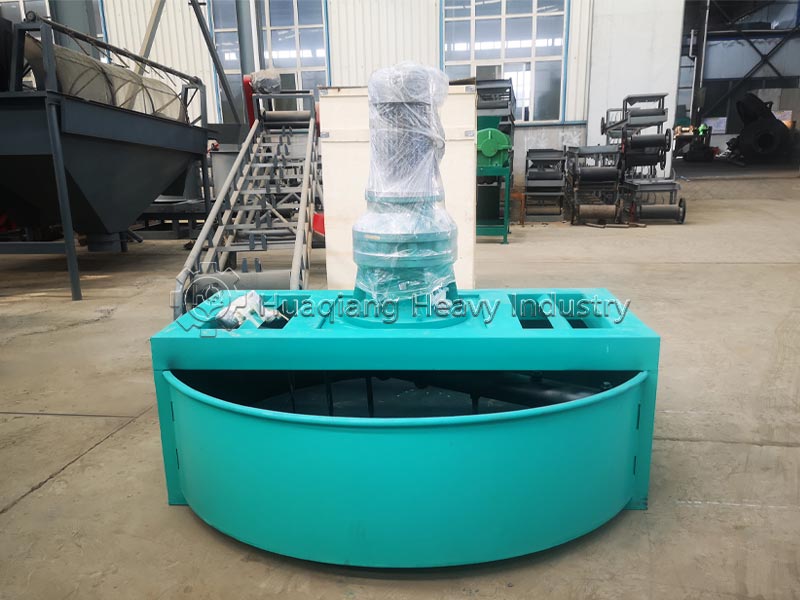
Different production processes and nutrient uniformity: Compound fertilizers require a dedicated NPK fertilizer production line. Nitrogen, phosphorus, potassium, and other raw materials undergo chemical synthesis reactions to form new compounds, which are then shaped by a fertilizer granulator. Nutrients are evenly distributed in each granule, with precise and controllable content. Blended fertilizers do not require chemical synthesis; they only need to be mixed evenly using a fertilizer mixer machine with two or more single fertilizers or compound fertilizers. The production process is simpler, but due to limitations in mixing accuracy, there may be localized uneven nutrient distribution.
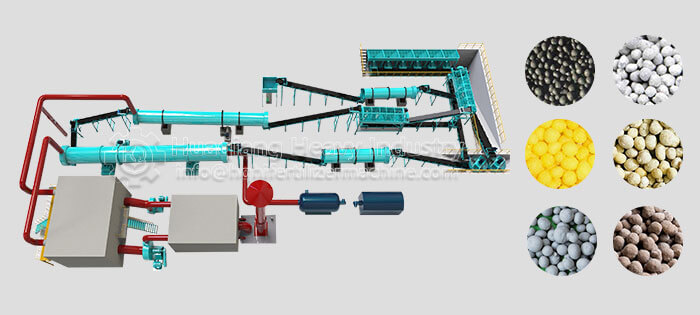
Different fertilizer release and application scenarios: Due to the high degree of nutrient integration, compound fertilizers have a stable and long-lasting effect, suitable for the entire growth period of field crops such as wheat and corn, reducing the need for frequent topdressing. Blended fertilizers allow for flexible adjustment of nutrient ratios according to the specific growth stage of the crop. For example, a high-potassium blended fertilizer can be used during the fruit-swelling stage of fruits and vegetables for rapid nutrient replenishment. However, the fertilizer release is relatively scattered, and application timing needs to be controlled to avoid nutrient loss.Selection recommendations: For precise and long-lasting nutrient supply, suitable for large-scale mechanized planting, choose compound fertilizers; for flexible nutrient adjustment, targeted fertilization at specific crop stages, or small-scale planting scenarios, choose blended fertilizers.