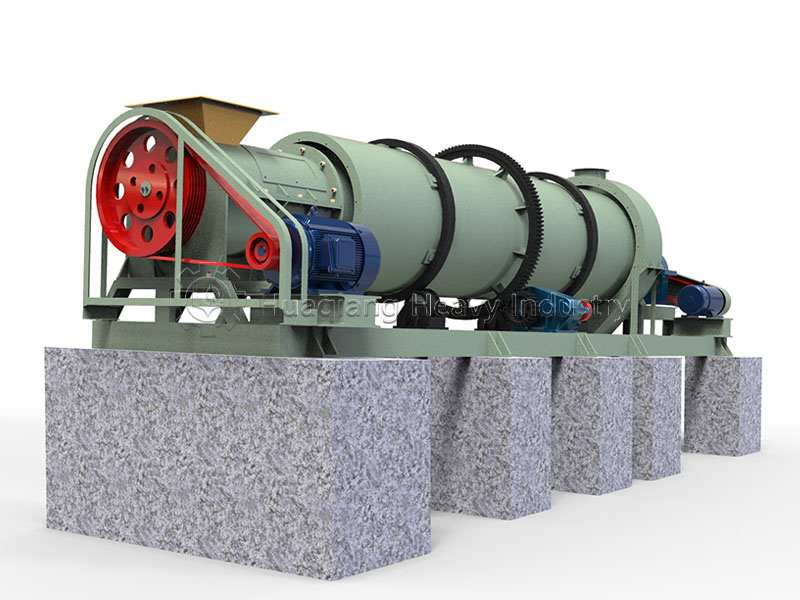
A brief discussion of the large wheel compost turner: A key driver for fertile soil regeneration
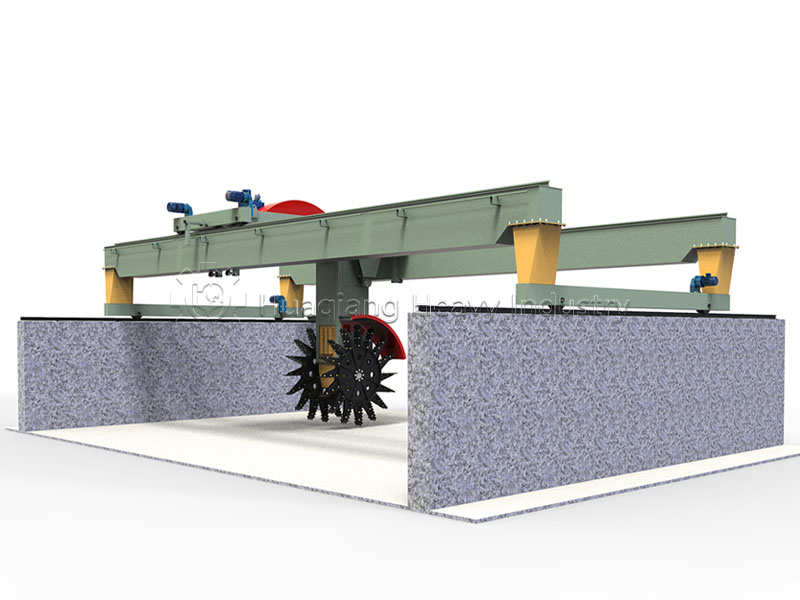
Upon entering a composting site, the large wheel compost turner often immediately catches the eye. Moving slowly and steadily, its massive rotating disc churns and scatters the material layer by layer, like a tireless dancer endlessly circling the composting stage.
The unique feature of this machine lies in its processing method—it completes the turning and scattering operation without needing to transfer the material elsewhere. As the disc rotates, air is naturally delivered deep into the material, and moisture evaporates evenly, creating an ideal living environment for microorganisms. This is a crucial step in the composting process, directly affecting the quality of subsequent granulation.
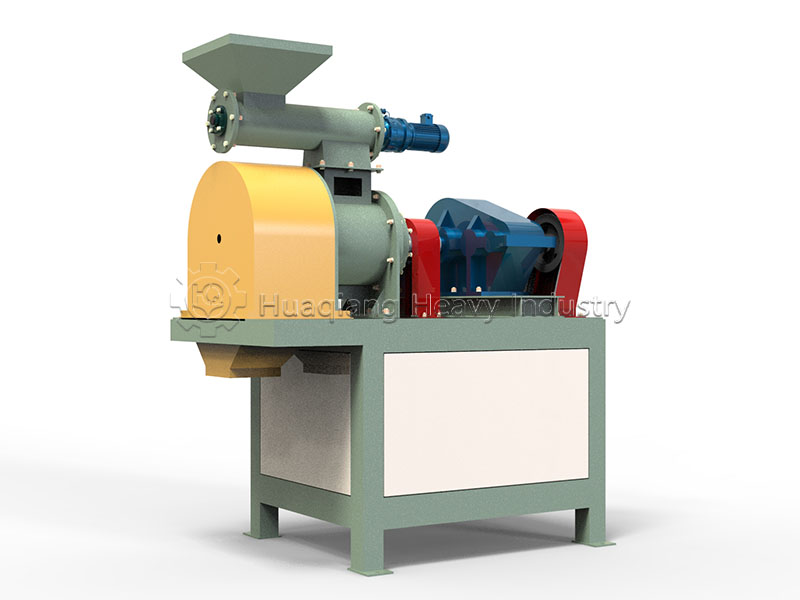
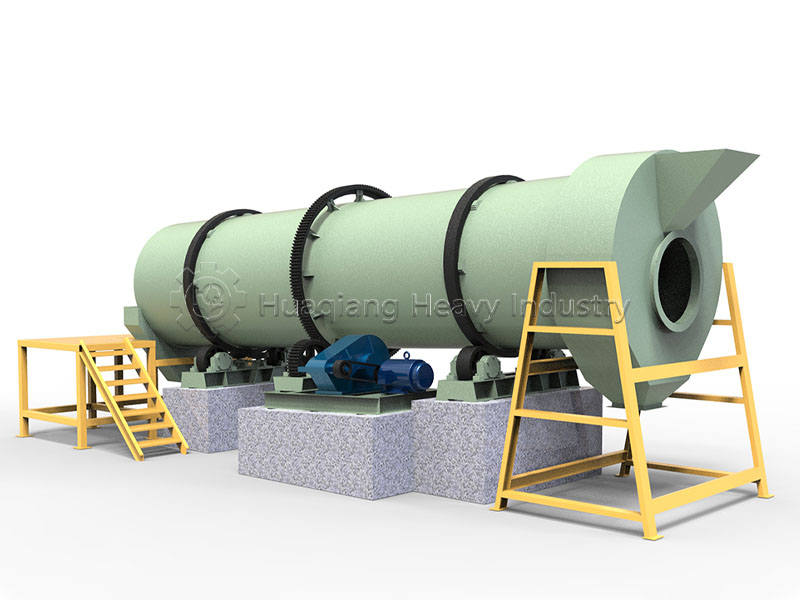
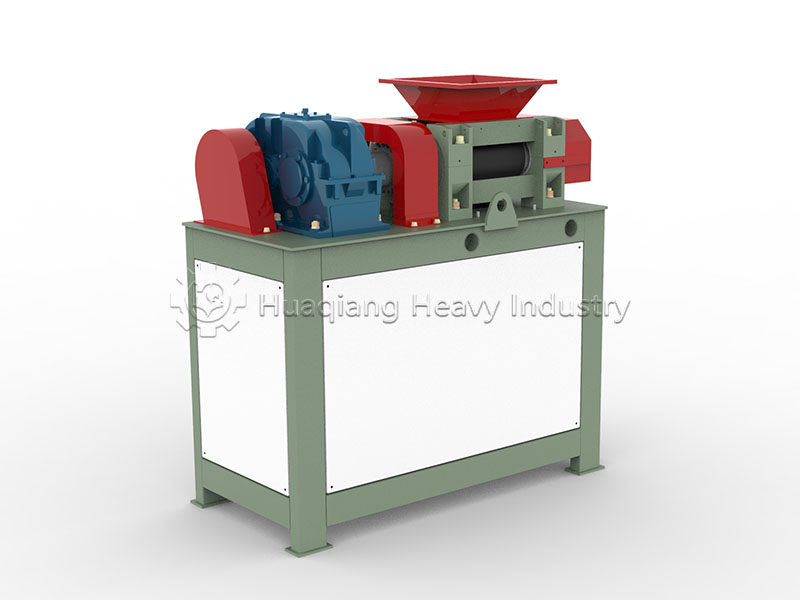
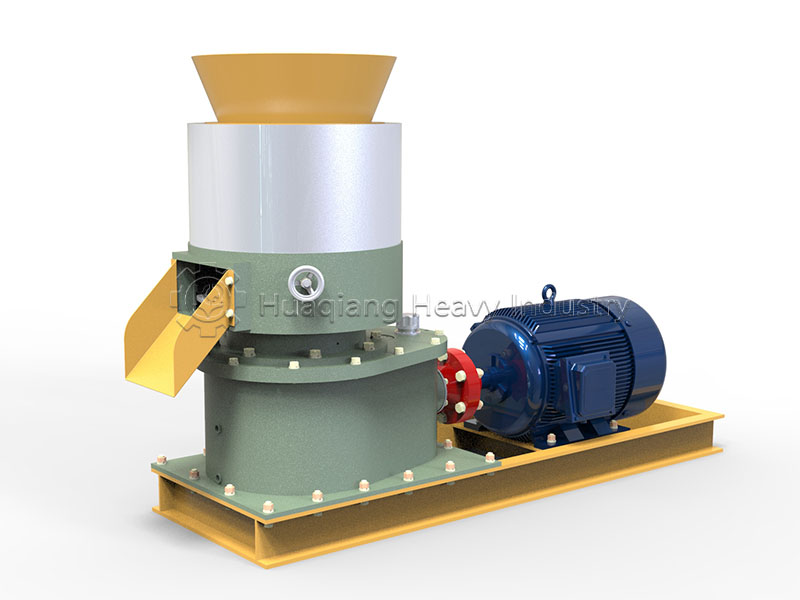
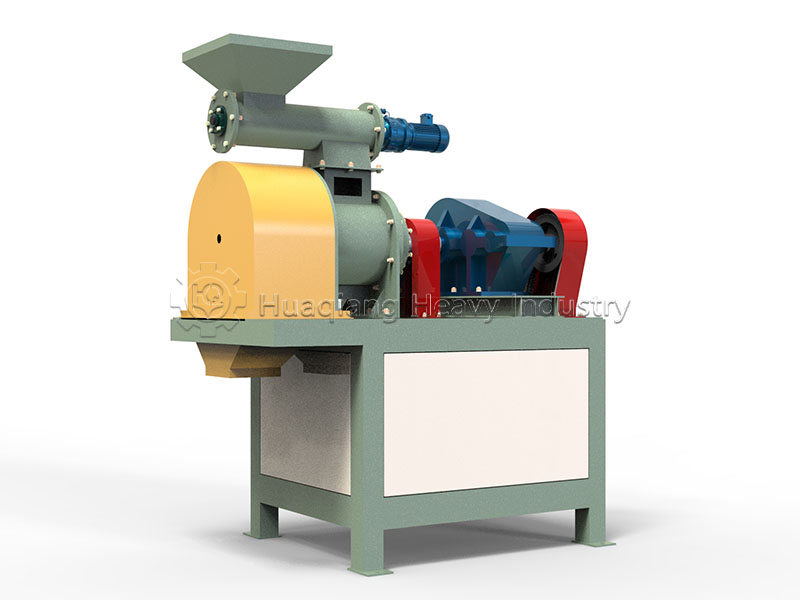
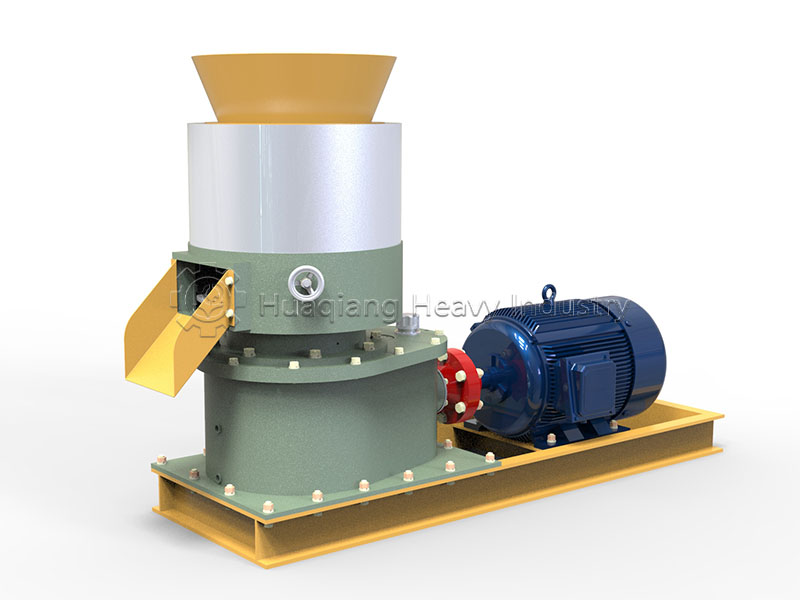
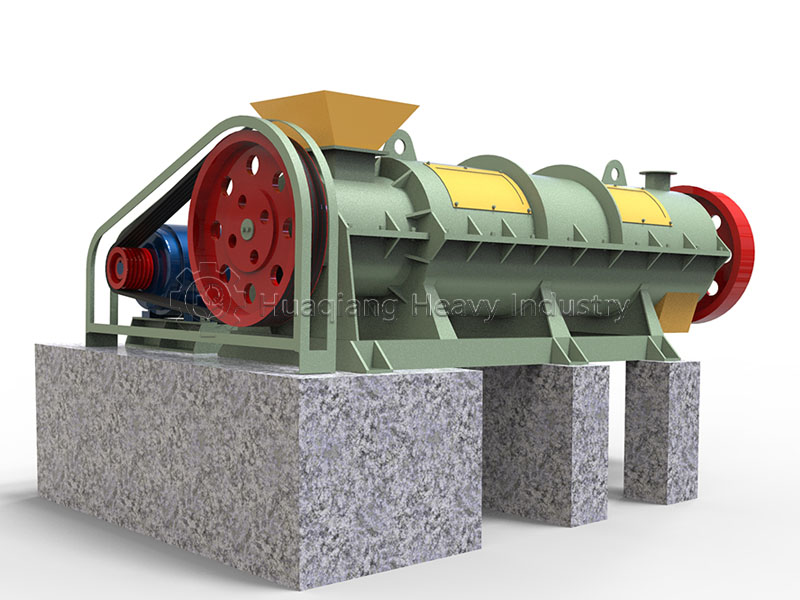
Speaking of granulation, different processes have their advantages and disadvantages. In organic fertilizer production, flat die pelleting machines are favored for their compact structure, suitable for small to medium-sized production lines. Ring die pelleting machines, on the other hand, occupy a place in large-scale production due to their stable granule quality and high output. For processing fertilizers with special formulations, the unique tumbling action of the rotary drum granulator can achieve even better granulation results.
These granulation devices each have their own strengths, but they all rely on thorough fermentation treatment in the early stages. The large wheel compost turner plays a crucial role in this preparation stage, and its uniform mixing lays a solid foundation for subsequent processes.