Disc Granulator: Why Is It Preferred?
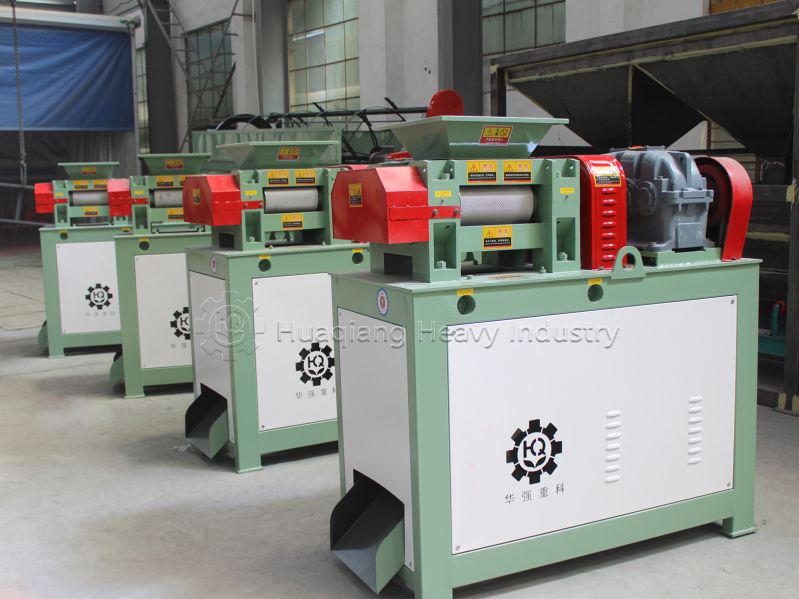
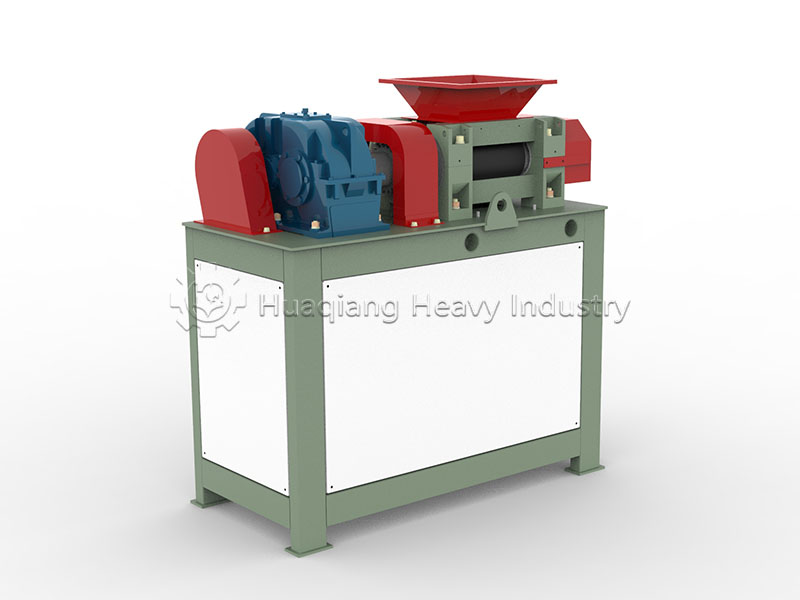
In modern fertilizer production, the disc granulator stands as a master craftsman, becoming the preferred equipment for numerous enterprises within the NPK manufacturing process. While the rotary drum granulator offers an alternative approach, the disc granulator’s unique design philosophy and exceptional performance for creating uniform fertilizer granules make it indispensable. For materials requiring fertilizer compaction, the fertilizer compactor and roller press granulator production line provide specialized solutions for fertilizer granules compaction. A reputable fertilizer machine manufacturer typically integrates both technologies into a comprehensive NPK fertilizer production line, ensuring optimal equipment selection for each production stage. This sophisticated fertilizer production machine ecosystem, whether utilizing a drum granulator or specialized fertilizer compaction machine, contains profound engineering wisdom that transforms powder materials into valuable agricultural nutrients through precise mechanical design and controlled agglomeration processes.
.jpg)
Precision Structure: Every Component Is Indispensable
Core Granulation Disc
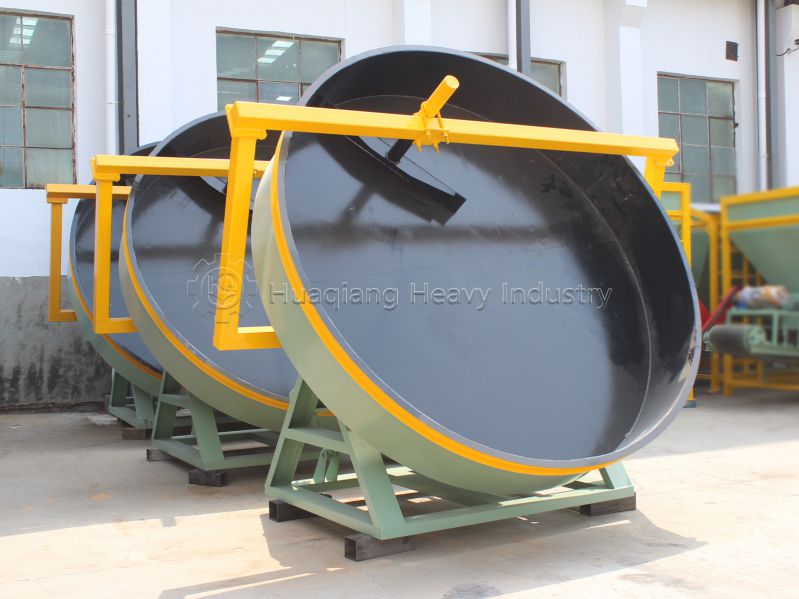
As the heart of the equipment, the granulation disc is welded from high-quality steel plates with wear-resistant lining on the inner wall, ensuring long-term stable operation. With diameters ranging from 1-5 meters, depths of 0.3-1.5 meters, and adjustable inclination angles between 30°-60°, it meets diverse production requirements.
Precision Transmission System
The transmission device, composed of motor, reducer, and pulley, ensures the granulation disc rotates steadily at 5-30 rpm. This precise power system is key to ensuring uniform particle quality.
Intelligent Control System
Equipped with advanced feeding devices and water spray systems, it achieves uniform material feeding through screw feeders or belt feeders, combined with precise water spraying to ensure optimal material moisture content.
| Component | Technical Parameters | Features |
| Granulation Disc | Diameter 1-5m, Inclination 30°-60° | Core working part with wear-resistant lining |
| Transmission System | Rotation Speed 5-30 rpm | Ensures stable operation and uniform particles |
| Frame Structure | Steel Section Welding | Provides stable support and equipment stability |
Outstanding Advantages: Redefining Granulation Standards
Excellent Pelletizing Effect
Particle sphericity exceeds 80%, smooth surface, high uniformity, and excellent strength
Easy and Flexible Operation
Simple and intuitive structure, precise control through speed and angle adjustment
Wide Adaptability
Processes various materials, from powders to viscous materials with perfect results
Energy Efficient Operation
Lower energy consumption compared to other equipment, more competitive operating costs
Particularly noteworthy is the remarkable flexibility disc granulators demonstrate when processing different materials. Whether dealing with fine powders or somewhat viscous raw materials, they can achieve optimal granulation results through precise adjustment of process parameters. This powerful adaptability ensures excellent performance in varying production environments.
Production Efficiency: Driving Force of Continuous Innovation
Disc granulators employ continuous production methods with hourly outputs ranging from several tons to dozens of tons, fully meeting production needs of different scales. Their efficient operation and stable product quality make them indispensable key equipment in modern fertilizer production lines. Meanwhile, the modular design concept makes equipment maintenance more convenient, significantly improving overall operational efficiency.
The disc granulator represents not only an outstanding example of mechanical engineering technology but also the perfect embodiment of modern production process wisdom. From precise component design to intelligent operating systems, from excellent pelletizing effects to efficient operational performance, every detail demonstrates the sophistication and innovation of engineering technology. As global fertilizer production continues to pursue efficiency, energy conservation, and environmental protection, disc granulators are consistently providing strong technical support for global agricultural production with their exceptional performance and reliable quality.