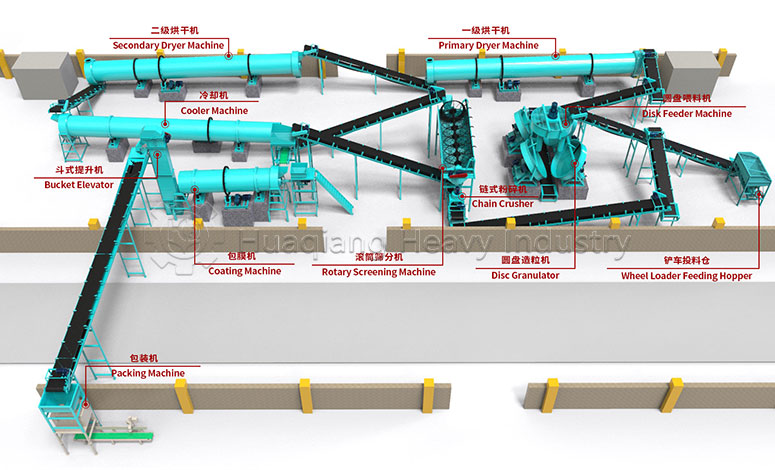
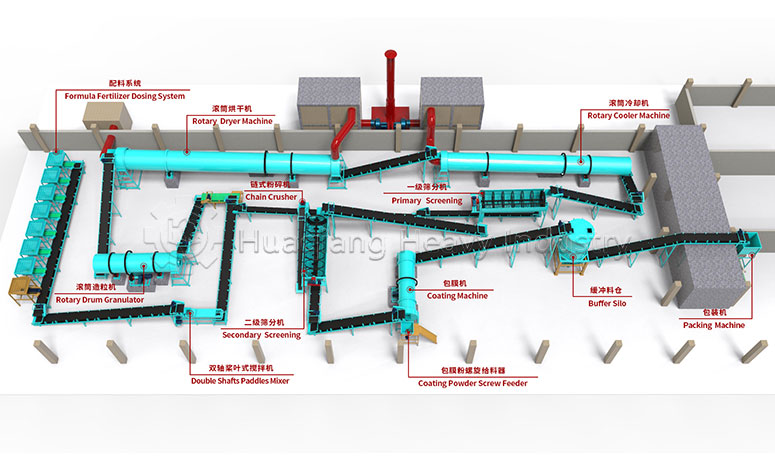
How windrow compost turning machines improve the efficiency of bio-organic fertilizer production lines?
In modern composting plants, windrow compost turning machines are quietly changing the traditional model of organic waste treatment. They are no longer simply turning tools, but a crucial link connecting waste with resource utilization.
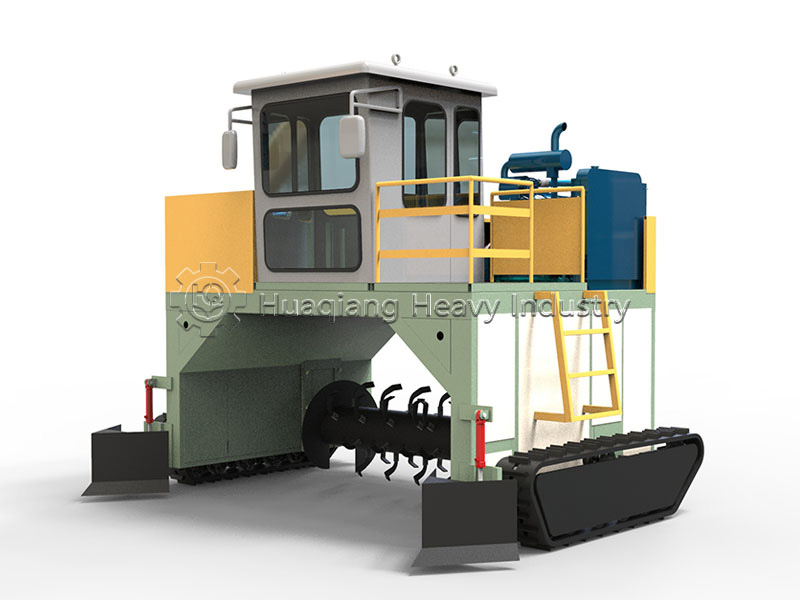
Unlike wheeled equipment, their unique tracked chassis offers significant advantages. On soft, uneven materials, the wide tracks effectively distribute pressure, preventing slippage. Whether in muddy conditions after rain or on loose piles, they can move stably, achieving continuous and efficient turning operations.
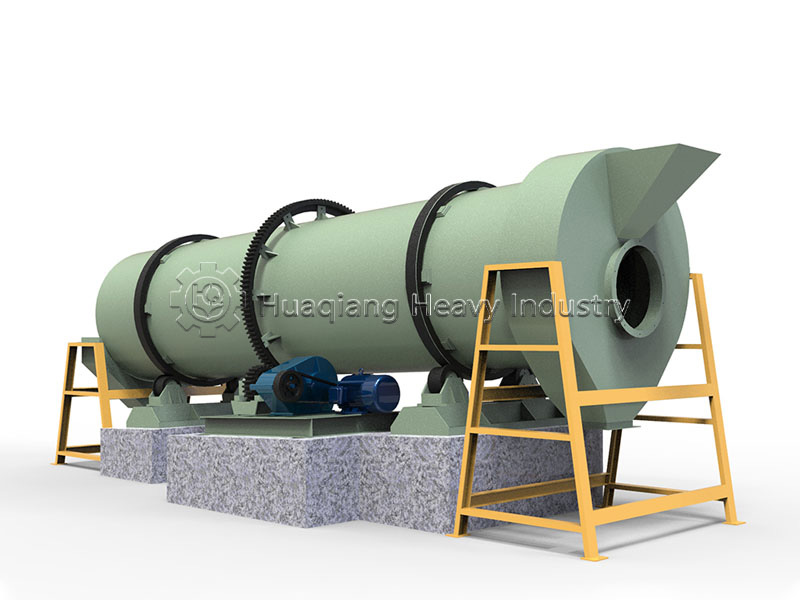
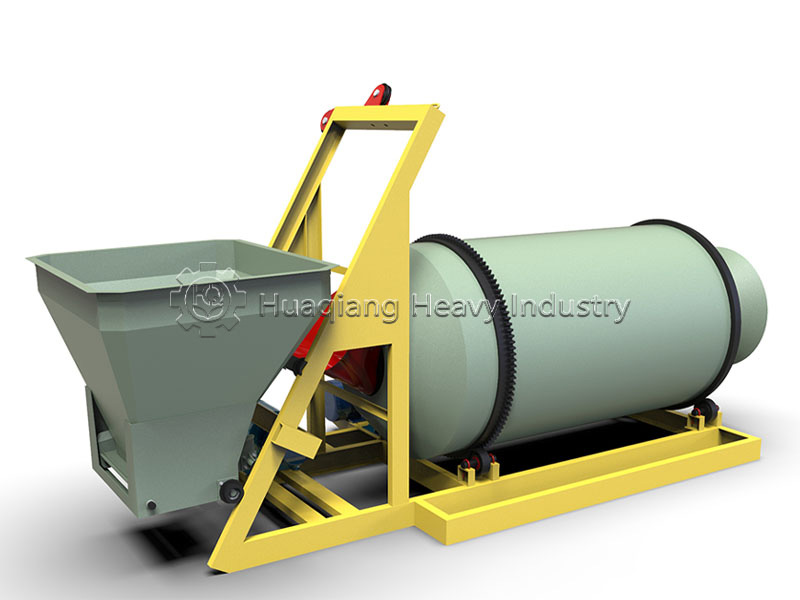
Through a powerful rotor system, the equipment evenly disperses and tosses the material, creating an ideal lifeline for aerobic microorganisms. This precise turning operation directly determines the quality of the raw materials for subsequent fertilizer granules compaction. When the finely fermented raw materials enter the new type organic fertilizer granulator, high-quality pretreatment ensures the final granule formation rate and quality.

In a complete bio-organic fertilizer production line, the windrow compost turning machine plays an indispensable pretreatment role. Working in conjunction with subsequent bio-organic fertilizer equipment, it forms a bridge between waste and high-value-added products.
This windrow compost turning machine symbolizes an upgrade in modern organic waste treatment methods, becoming a crucial link in the bio-organic fertilizer production line, bridging the gap between upstream and downstream processes, on the path to promoting sustainable agricultural development.