From powder to granules: How fertilizer granules compaction technology is reshaping agriculture?
Step into the fields, and you’ll find that fertilizers today are vastly different. Uniform, round granules have replaced the dusty powder of the past—this is thanks to the revolutionary fertilizer granules compaction technology.
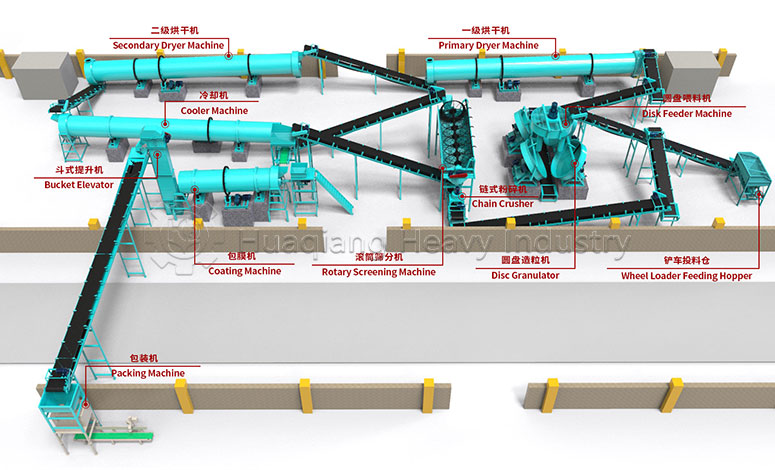
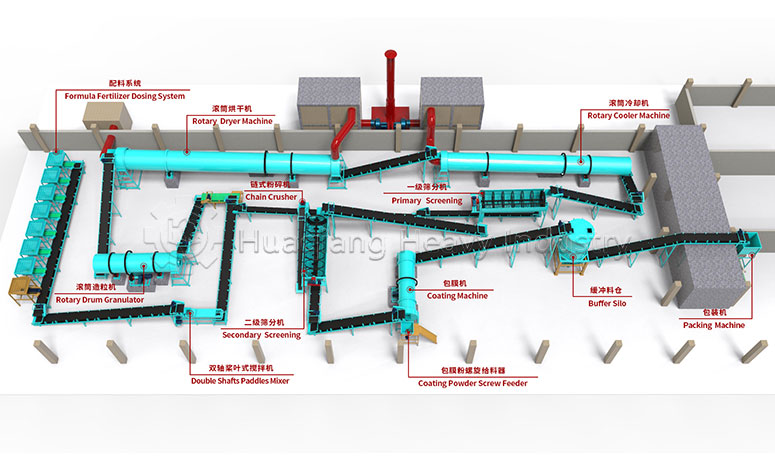
Fertilizer granules compaction technology uses mechanical pressure to directly press various raw materials into regular granules. This method eliminates the need for drying, ensuring complete nutrient retention. This physical forming method is particularly suitable for organic fertilizer production.

In modern fertilizer production, different product lines each have their own characteristics. New type organic fertilizer granulators can process diverse raw materials such as straw and livestock manure, producing granules that are not only easy to apply but also significantly reduce environmental pollution. In NPK fertilizer production lines, fertilizer granules compaction technology achieves precise proportions and uniform distribution of nutrients such as nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium, ensuring each granule contains balanced nutrients. As for bio-organic fertilizer production lines, they successfully maintain the activity of functional bacteria during the granulation process, achieving a perfect combination of organic carriers and microorganisms.
The changes brought about by these technological advancements are evident. The transformation from powder to granules may seem like just a change in form, but it is actually a microcosm of precision agricultural management. With the continuous advancement of fertilizer granules compaction technology, fertilizers are nourishing our land in a more efficient and environmentally friendly way.