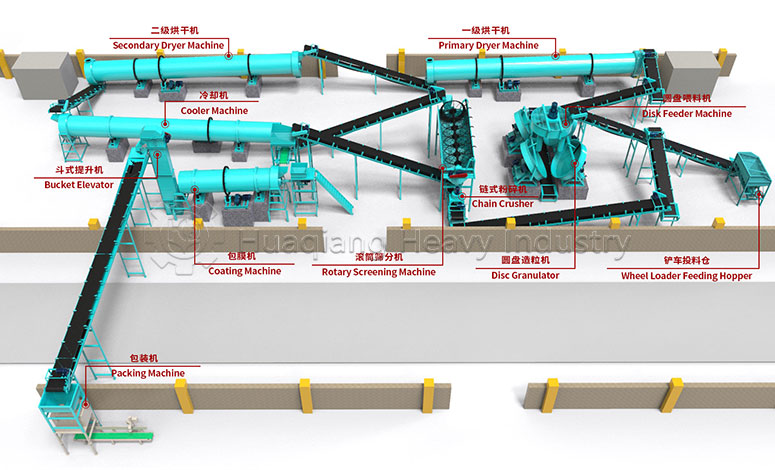
From manure to “Golden Granules”: The modern transformation of organic fertilizer
Once upon a time, organic fertilizer processing was synonymous with “piles of manure, relying on the heavens to decompose.” Today, this traditional industry is undergoing a silent technological revolution, transforming polluted agricultural waste into uniformly sized, consistently effective black “golden granules.”
This transformation begins with highly efficient bio-organic fertilizer equipment. These systems constitute an intelligent “fermentation workshop.” Through precisely controlled turning, ventilation, and temperature control systems, these devices create the ideal breeding environment for microbial communities.
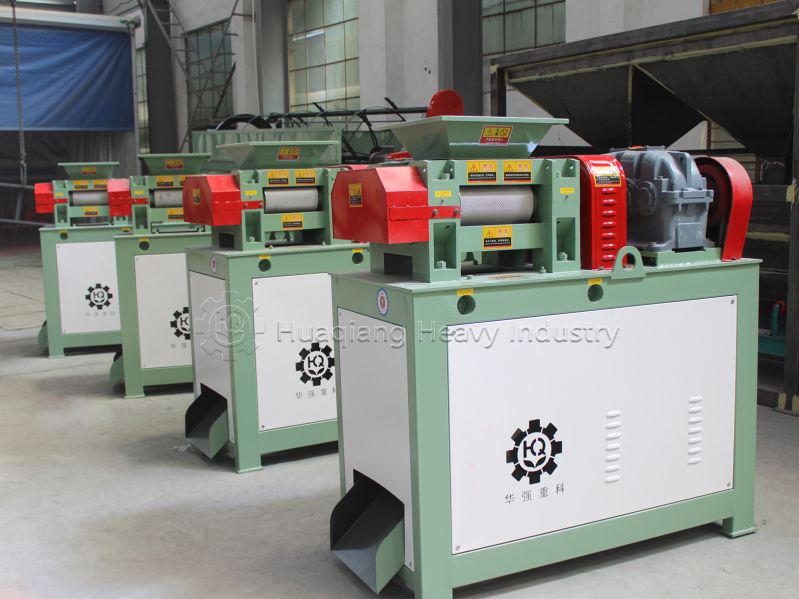
However, powdered organic fertilizer still faces problems such as large volume, easy dust generation, and inconvenience in application. This is where the core step in the process—fertilizer granules compaction—comes in. This process is like “shaping” the fertilizer, using powerful mechanical pressure to tightly compress loose powdery raw materials into uniformly sized solid granules.
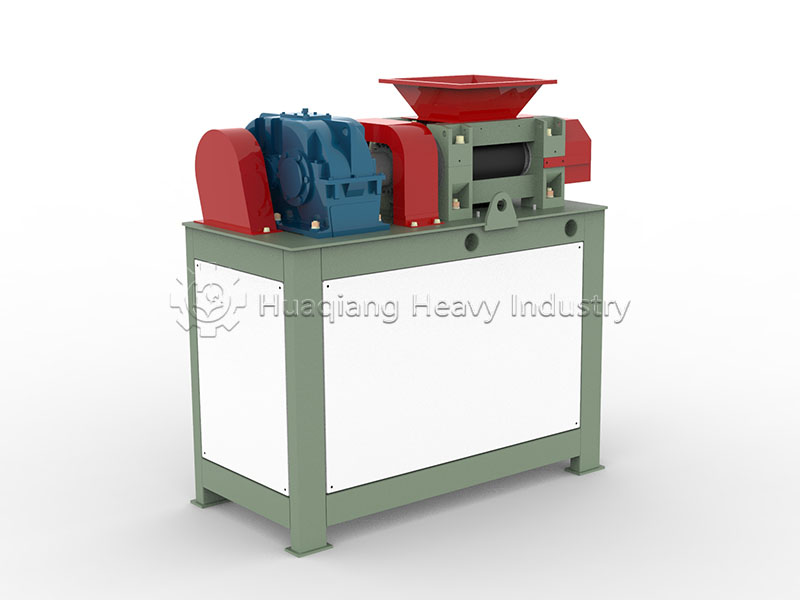

Fertilizer granules compaction is far more than simple physical molding. The ingenious use of pressure creates an appropriate compactness within the granules, ensuring they are not easily broken during transportation and storage, while also guaranteeing that they will moderately disintegrate upon contact with water after being applied to the soil, slowly releasing nutrients.
From fermentation using modern bio-organic fertilizer equipment to achieving its ideal physical form through precise fertilizer granules compaction, organic fertilizer has finally completed a remarkable transformation from a crude raw material to a standardized commodity.