In the vast landscape of fertilizer production, the fertilizer mixer machine plays a silent yet crucial role. It doesn’t possess the power of a crusher, nor the shaping ability of a granulator, but it is the core element determining the homogeneity of the product.
Walk into any modern NPK fertilizer production line, and you’ll almost always find it in a core section. Various precisely measured nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium raw materials, along with trace amounts of additives, are fed into it. Whether it’s the powerful agitation of the twin-screw agitation or the uniform tumbling of the horizontal drum, the goal is crystal clear: to fuse materials of varying shapes and densities into a uniform, nutrient-rich mixture in the shortest possible time.
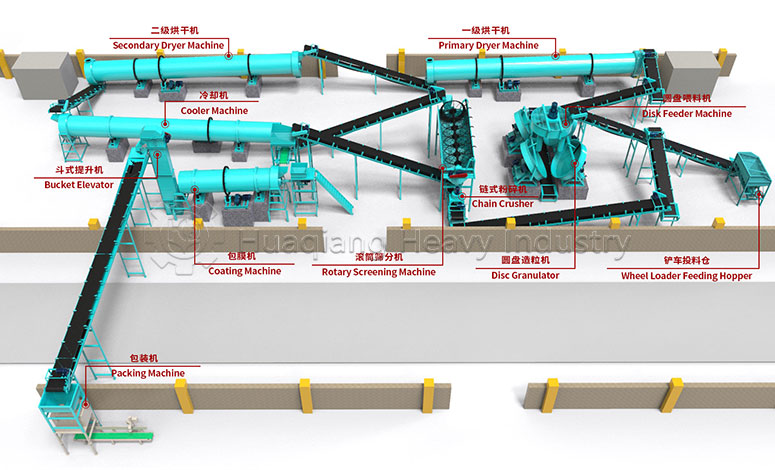
When the scene shifts to a bio-organic fertilizer equipment array, the fertilizer mixer machine takes on a more nuanced role of “harmonizing.” The materials processed here are more complex—fermented organic matter, livestock manure, peat moss, or microbial residue, all with varying moisture content and loose textures. The mixer needs to provide gentler and more sustained agitation here to ensure that the organic raw materials come into full and even contact with the appropriate amount of functional microbial agents, nitrogen-fixing and phosphorus-solubilizing bacteria, and other microbial communities, avoiding localized over-concentration or under-concentration of the microbial community.
Therefore, whether it’s an NPK fertilizer production line pursuing precise chemical ratios or a bio-organic fertilizer equipment emphasizing biological activity, the mixer is an indispensable “link.”