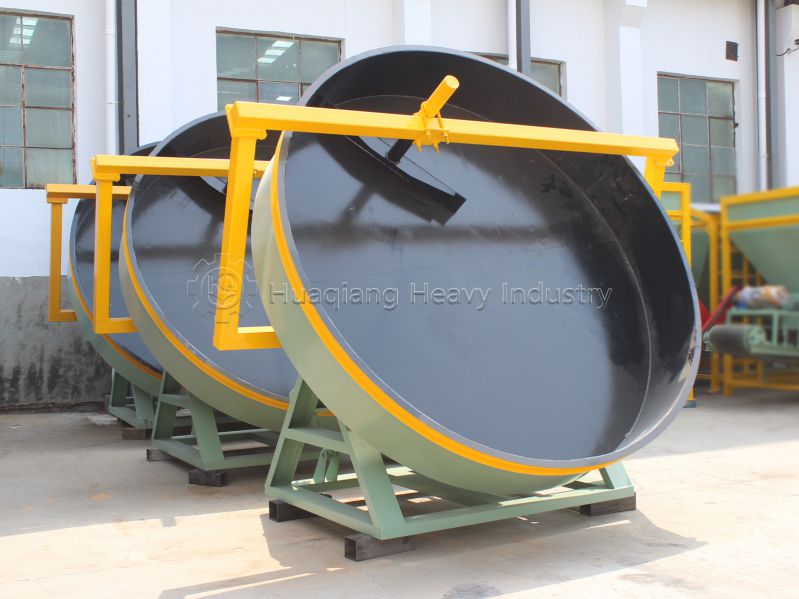
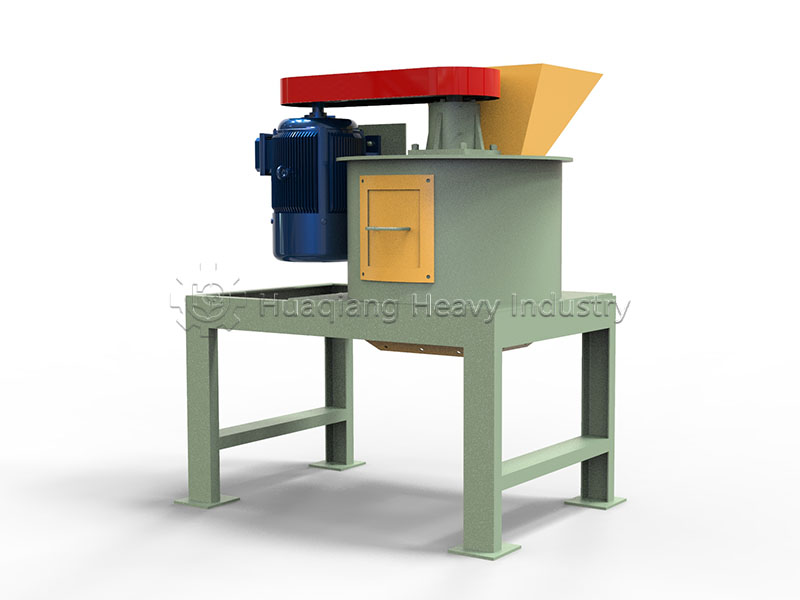
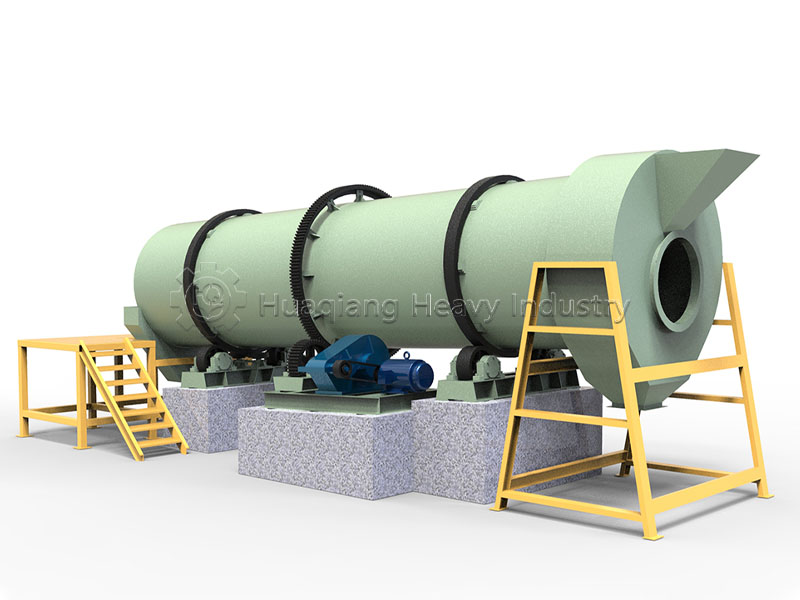
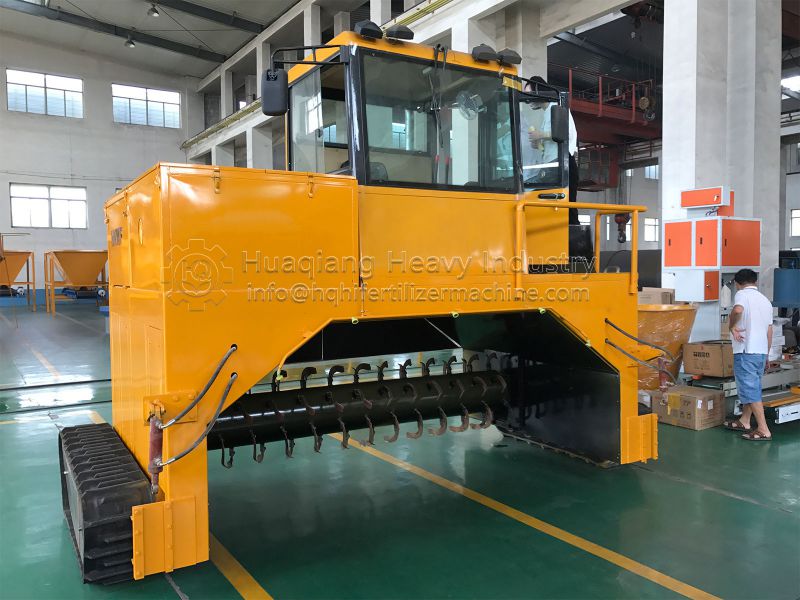
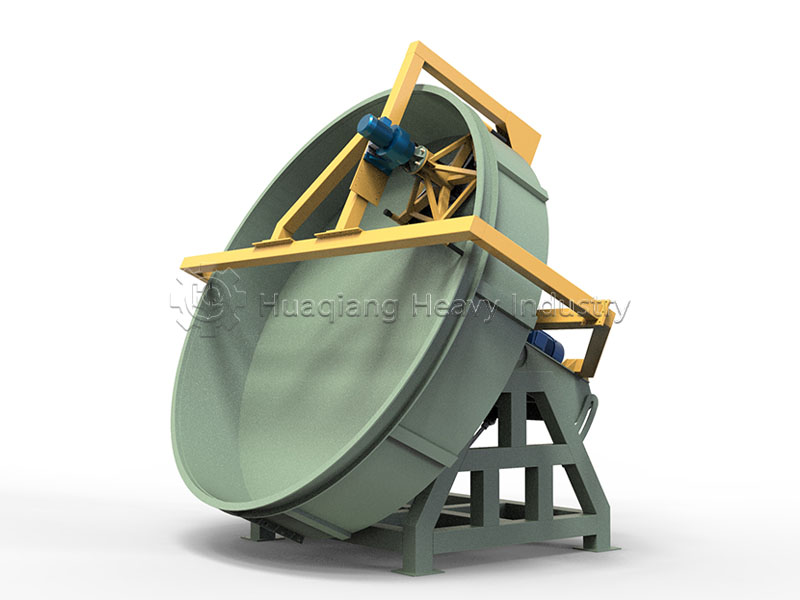
The “Competition” between large wheel compost turners and traditional compost turning equipment
In the field of organic waste treatment, compost turning equipment is a critical tool. The emergence of large wheel compost turning machines has disrupted the traditional compost turning system, creating a fierce competition with it.
Traditional trough compost turning machines typically require the construction of fixed fermentation tanks, which not only limits the equipment’s flexibility but also takes up a significant amount of site space. For example, a small organic waste treatment project with a daily processing capacity of 10 tons would require the construction of at least two fermentation tanks, each 10 meters long and 3 meters wide. Including the spacing between the tanks and the operating space, the total area required is approximately 100 square meters.
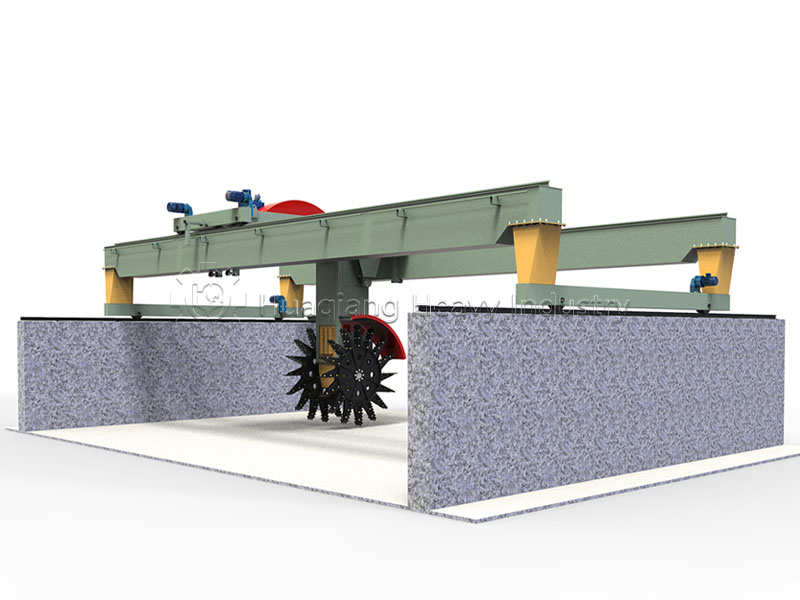
Large wheel compost turning machines, on the other hand, have relatively low site requirements. Without the need for fixed fermentation tanks, they can operate in more open areas. To process the same 10 tons of organic waste, a large wheel compost turning machine may only require approximately 60 square meters of site space, significantly saving space.
Traditional compost turning equipment has a relatively limited turning range, typically 5-10 meters wide and 1-1.5 meters deep. Large-wheel compost turning machines, on the other hand, can reach widths of up to 30 meters and depths of 1.5-3 meters, enabling them to cover a wider area and greater depths.
Conventional equipment can have blind spots, resulting in incomplete fermentation of some materials. Large wheel compost turning machines, through symmetrical turning and a speed-adjustable, shifting trolley, achieve seamless turning, ensuring more even mixing and more complete fermentation.








