The three core types of fertilizers: Characteristics and applications
Fertilizers are the “nutritional cornerstone” for crop growth, and scientifically classifying fertilizer types is a prerequisite for rational fertilization. Based on their source, composition, and mechanism of action, fertilizers can be mainly divided into three categories: organic fertilizers, chemical fertilizers, and bio-organic fertilizers.
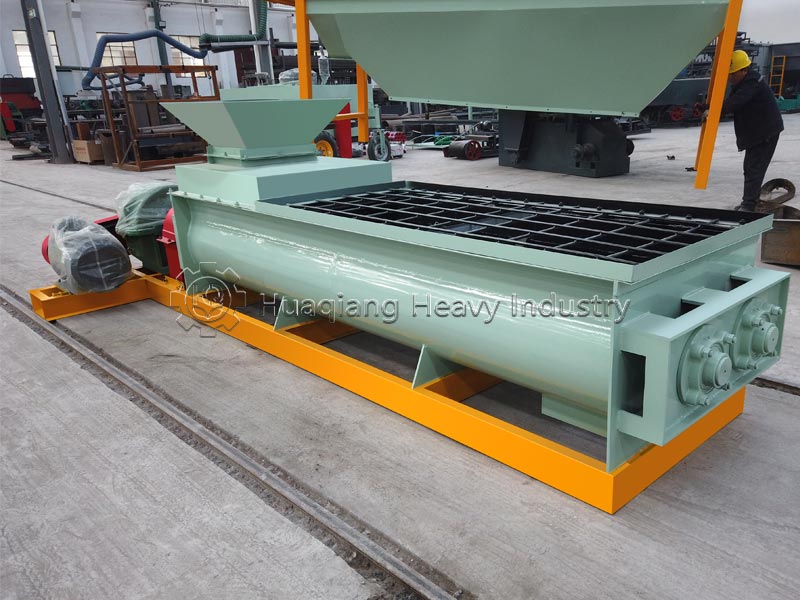
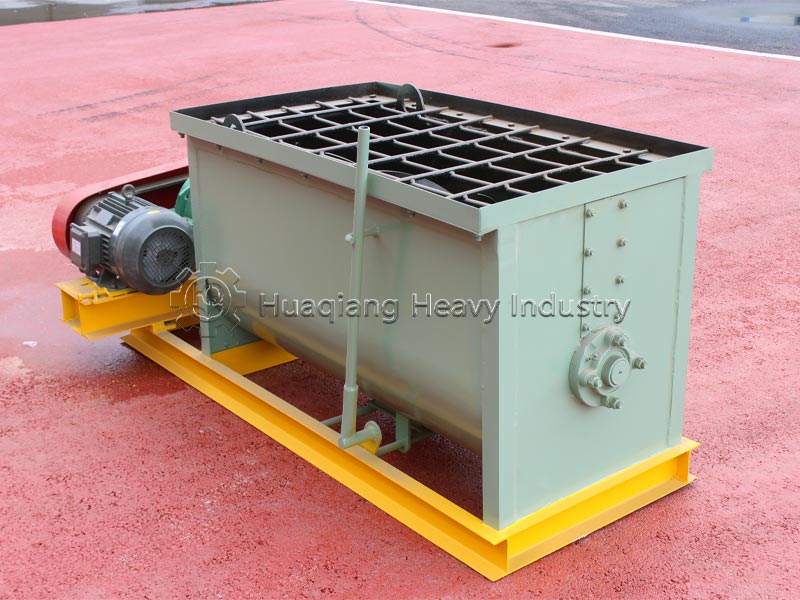
Organic fertilizers originate from animal and plant residues or decomposed waste. Their raw materials include livestock manure, crop straw, distiller’s grains, and kitchen waste, which are fermented and decomposed through organic fertilizer production lines to provide comprehensive nutrients. Organic fertilizers not only contain macronutrients such as nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium, but are also rich in micronutrients and organic matter. They are characterized by their mild and long-lasting effect, improving soil structure, promoting microbial activity, and enriching soil fertility with long-term use, making them suitable for base fertilization of various crops.
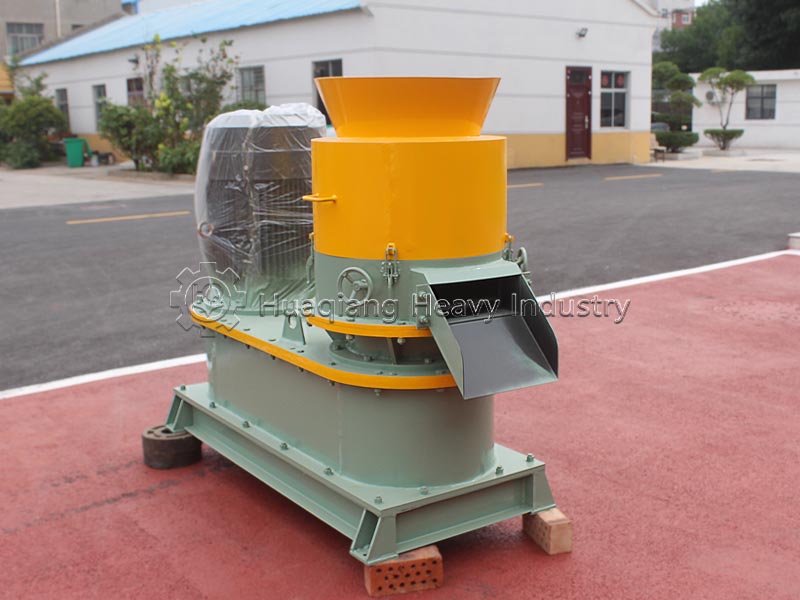
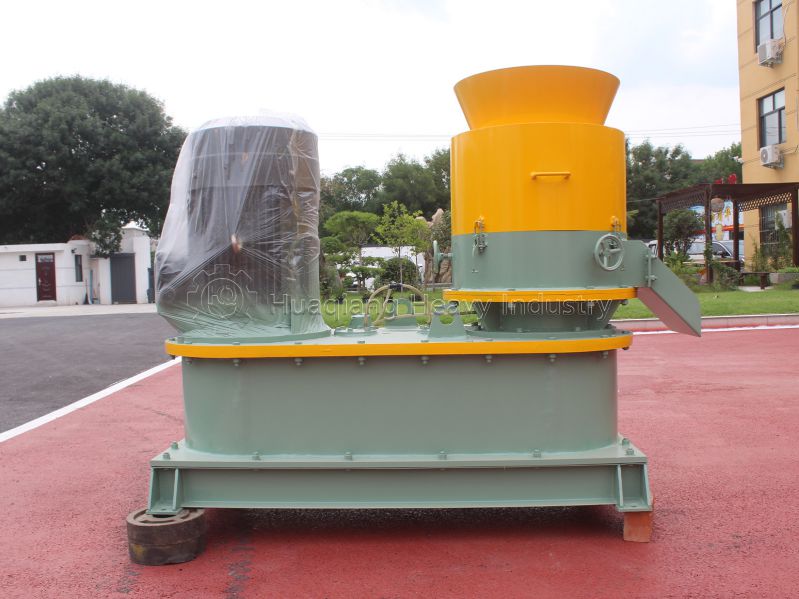
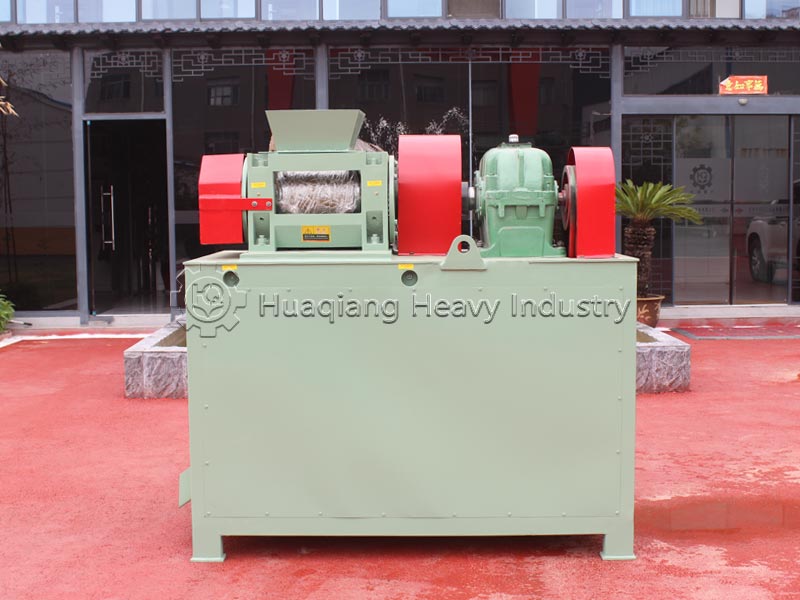
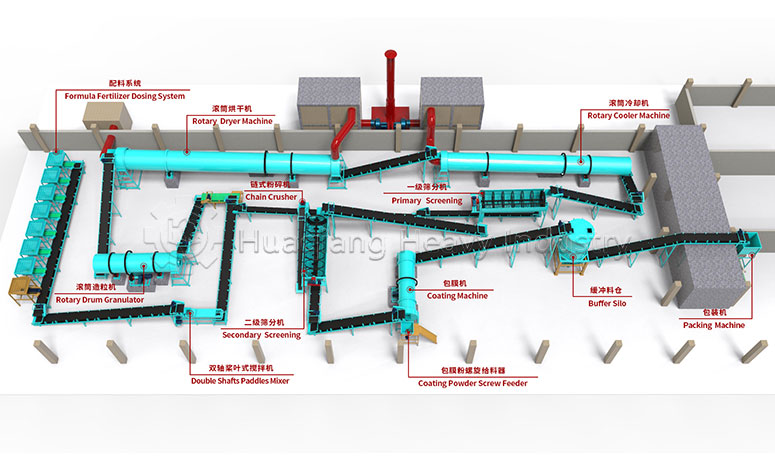
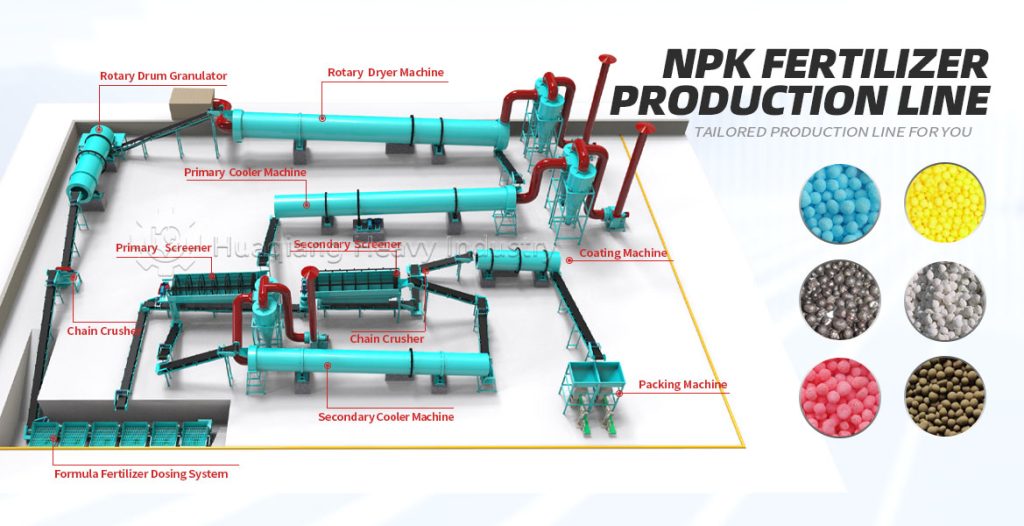
Chemical fertilizers are produced through industrial synthesis or mineral processing and are one of the mainstream fertilizers in modern agriculture. Based on nutrients, they can be divided into nitrogen fertilizers, phosphorus fertilizers, potassium fertilizers, and NPK compound fertilizers. NPK compound fertilizers are often precisely formulated and processed by NPK fertilizer production lines, providing single nutrients at high concentrations. Chemical fertilizers are characterized by their fast and direct effect, quickly alleviating nutrient deficiencies in crops and precisely meeting the nutrient needs of crops at different growth stages.
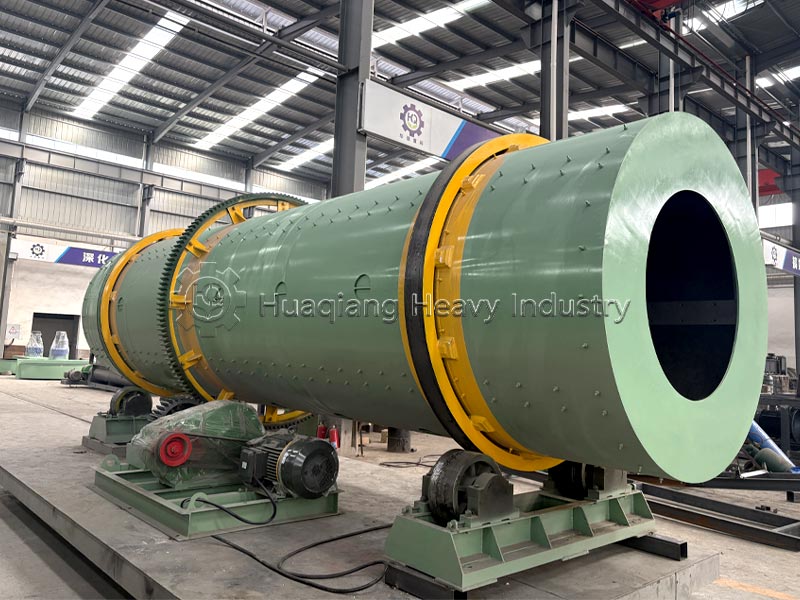
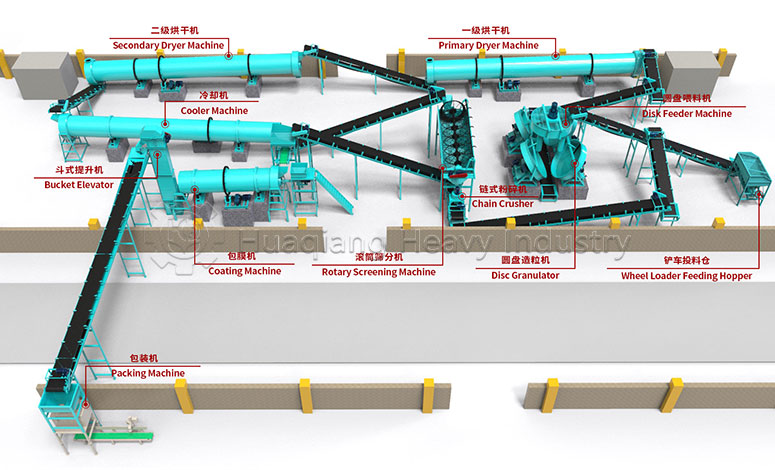
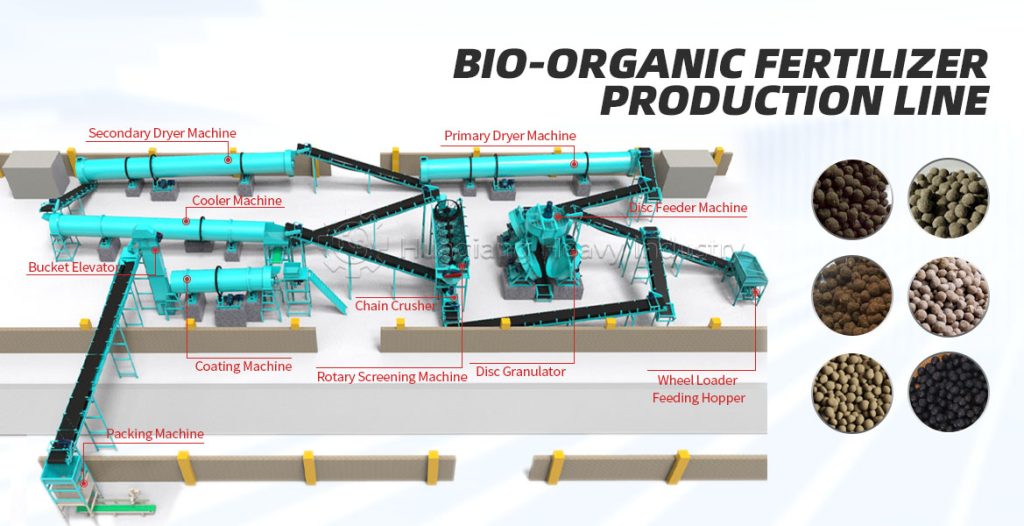
Bio-organic fertilizers, as an important category of high-quality organic fertilizers, can be specially processed by bio-organic fertilizer production lines, better preserving beneficial microorganisms and active ingredients. Their core components can activate fixed nutrients in the soil, inhibit harmful pathogens, and promote crop root development and improve nutrient absorption efficiency. They are characterized by being green and environmentally friendly, and are often used in combination with organic fertilizers and chemical fertilizers to help achieve improved quality, increased efficiency, and sustainable farming.